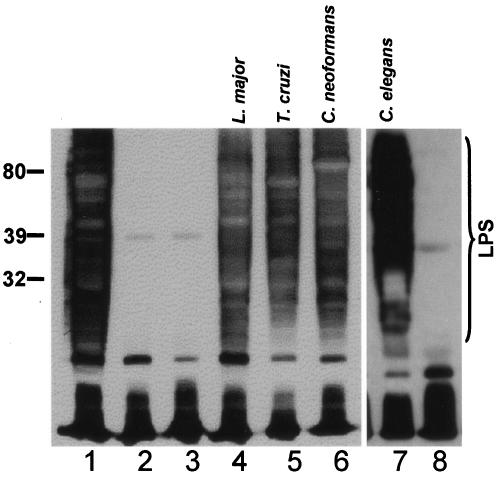
FIG. 3.
In vivo rescue of Galf-dependent LPS synthesis in E. coli. Bacterial lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis with rabbit anti-Klebsiella galactan I antisera as described in Materials and Methods. The migration of molecular mass markers (in kDa) is shown on the left, and the region corresponding to migration of LPS is shown by the bracket on the right; the antiserum also reacts with low-molecular-weight material (perhaps lipid A and LPS core), but the identification of O antigen is unequivocal. All strains derive from the E. coli rfb deletion strain CWG288. Plasmids introduced were as follows: lane 1, pWQ71 (intact Klebsiella rfb locus; positive control); lane 2, pWQ70 (pWQ71 with deletion inactivating GLF); lane 3, pWQ70+pET3a (vector control); lane 4, pWQ70+pET3a-LmjGLF; lane 5, pWQ70+pET3a-TcGLF; lane 6, pWQ70+pET3a-CnGLF; lane 7, pWQ70+pET3a-CeGLF; and lane 8, pWQ70 + inactive mutant pET3a-CeGLF (clone 1.1, strain B3597, which contains a 1-nt deletion at position 129 introducing a premature stop amongst other PCR-generated mutations). The experiment shown in lanes 7 to 8 was performed separately from those shown in lanes 1 to 6.