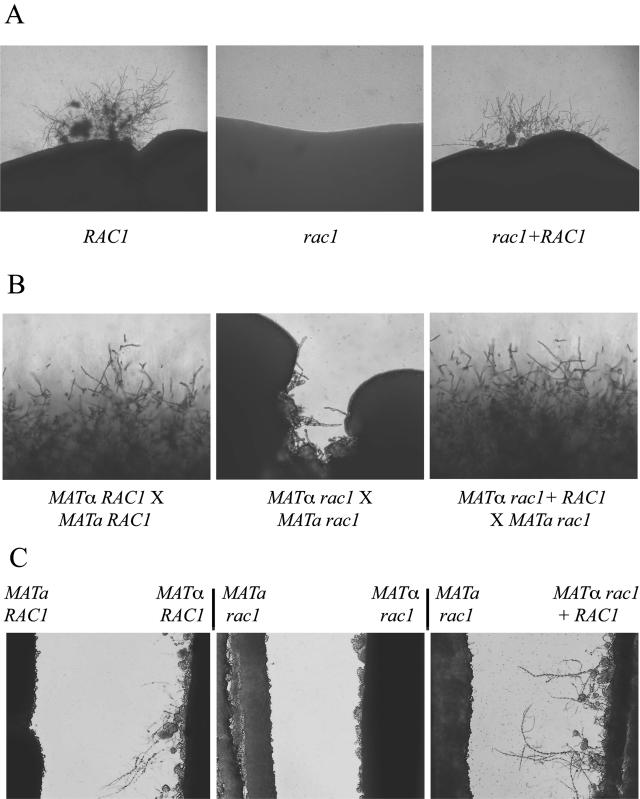
FIG. 3.
Rac1 is required for hyphal differentiation. (A) Haploid fruiting. The RAC1 wild-type, rac1 mutant, and rac1+RAC1 reconstituted strains were incubated for 3 weeks on filament agar. The edges of the culture patches were photographed to assess for filamentation due to haploid fruiting (40×). (B) Mating. The effect of a rac1 mutation on the mating process was assessed by coculturing MATα and MATa strains on V8 mating medium. Each strain possessed either a wild-type (RAC1) or a mutant (rac1) allele. The edges of the mating patches were assessed at 7 days for mating filamentation (100×). (C) Pheromone-induced hyphal formation. MATa and MATα strains were streaked on filament agar in close proximity to one another without physically touching. The cellular response to diffusible pheromone was assessed in this confrontation assay at 48 h (100×).