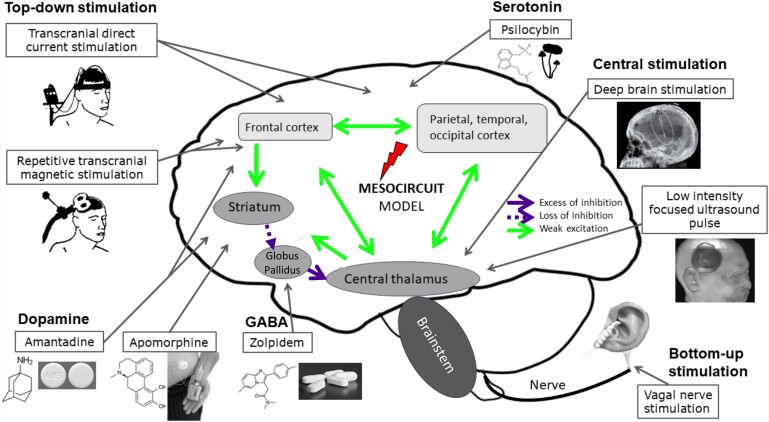
Figure 4.
Possible treatments tested for the therapy of patients with disorders of consciousness and their effect on the mesocircuit. Pathways of weakened excitation (green, solid) and excessive (purple, solid; only between globus pallidus and central thalamus) or loss (purple, dashed) of inhibition that characterize patients with a DoC are shown in the mesocircuit model. From the top right, going clock-wise is shown: the serotonin system that is affected by psilocybin and acts cortically; central stimulation through deep brain stimulation (DBS) acts mostly on the thalamus; low-intensity focused ultrasound also affects the thalamus; vagal nerve stimulation stimulates the brainstem by nerve stimulation (latter three are bottom-up processes); the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic drug zolpidem targets the globus pallidus; dopaminergic drugs amantadine and apomorphine act on the striatum, while the former also affects the frontal cortex; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) act cortically and stimulate activity in a top-down fashion. Figure adapted from 127.