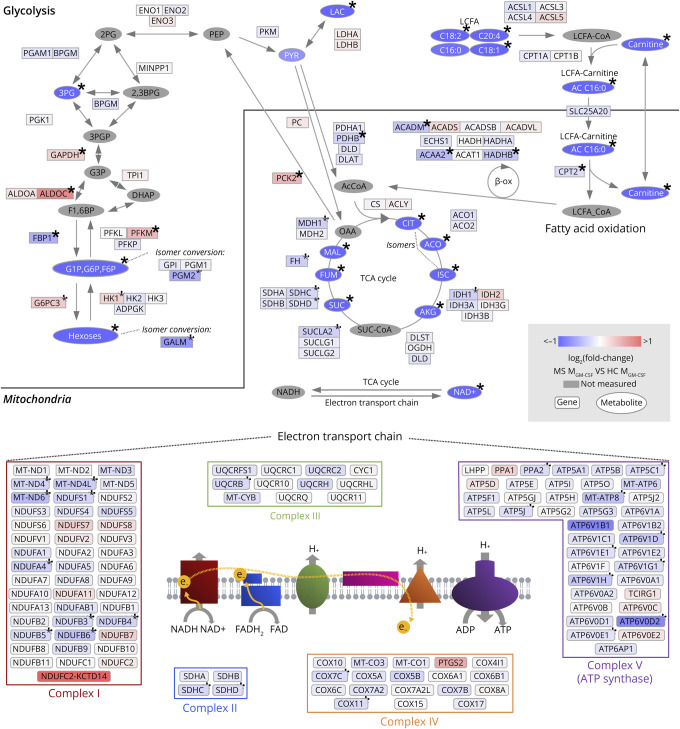
Figure 7. MS Homeostatic-Like Macrophages Show Several Signs of Alteration in Both the TCA Cycle and Respiratory Chain at the Gene Expression and Metabolic Levels.
Genes and metabolites included in the KEGG pathways, glycolysis, fatty acid degradation, TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, are organized according to pathways. Each element is colored to indicate fold change in MS MGM-CSF relative to HC (Δlog2(FC), overexpression in red, underexpression in blue). Genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are organized into the complexes in which their gene products take part. Genes that were not expressed in at least 1 sample were excluded from the figure. *Significantly altered genes (q < 0.05) in differential expression analysis (genes) or one-way ANOVA (metabolites). HCs n = 12 (metabolites) or 11 (genes); patients with MS n = 13 (metabolites) or 29 (genes). 2,3BPG = 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid; 2 PG = 2-phosphoglyceric acid; 3 PG = 3-phosphoglyceric acid; 3PGP = 3-phospho-d-glyceroyl phosphate; AcCoA = acetyl coenzyme A; ACO = aconitate; AKG = alpha-ketoglutarate; CIT = citrate; DHAP = dihydroxyacetone phosphate; F1,6BP = fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; FUM = fumarate; G1P = glucose-1-phosphate; G3P = 3-phosphoglycerate; G6P = glucose-6-phosphate; HC = healthy controls; ISC = isocitrate; LAC = lactate; LCFA = long-chain fatty acid; MAL = malate; MS = patients with MS; OAA = oxaloacetate; OXSUC = oxalosuccinate; PEP = phosphoenolpyruvic acid; PYR = pyruvate; SUC = succinate; SUC-CoA = succinyl coenzyme A; β-ox = beta-oxidation.