Abstract
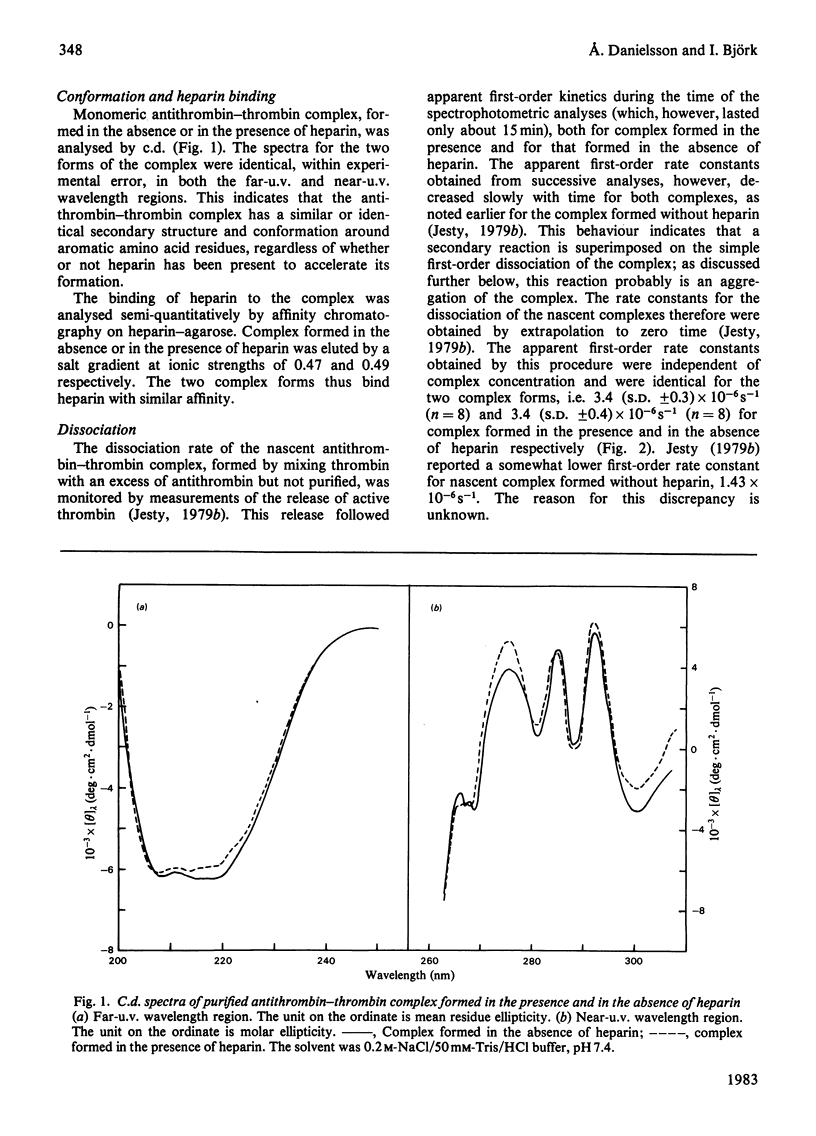
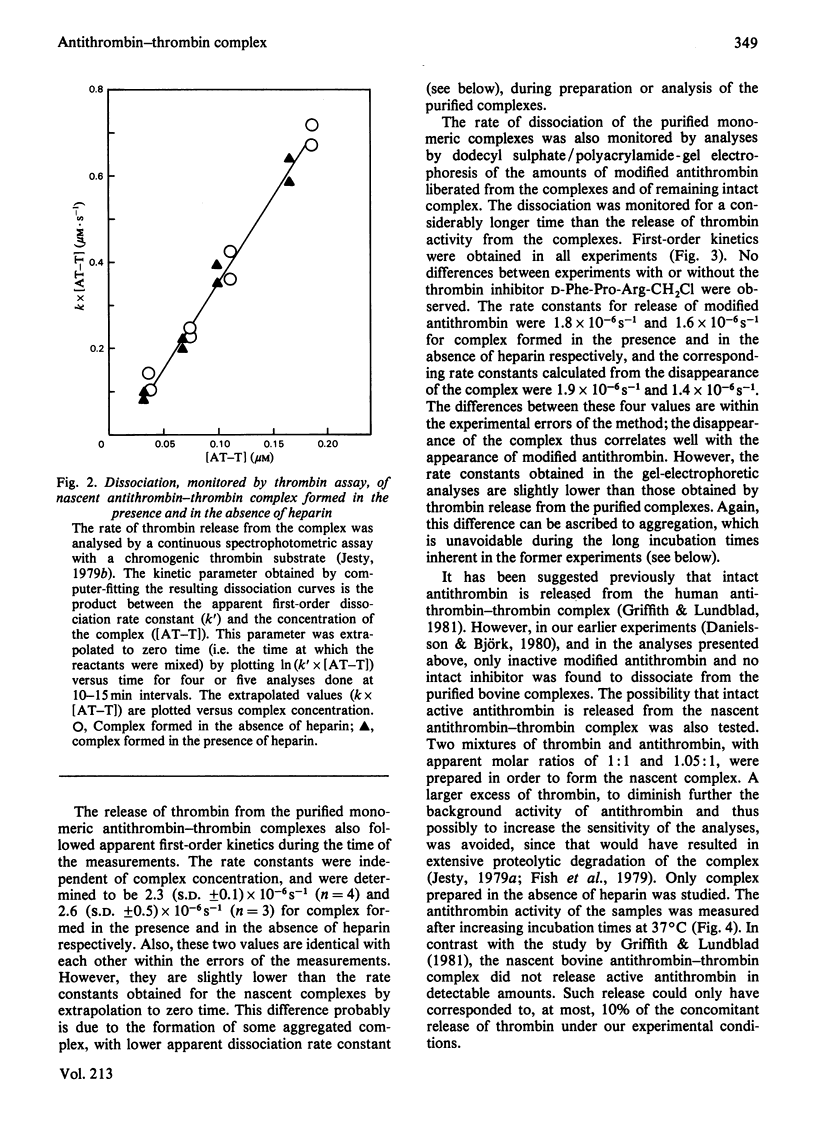
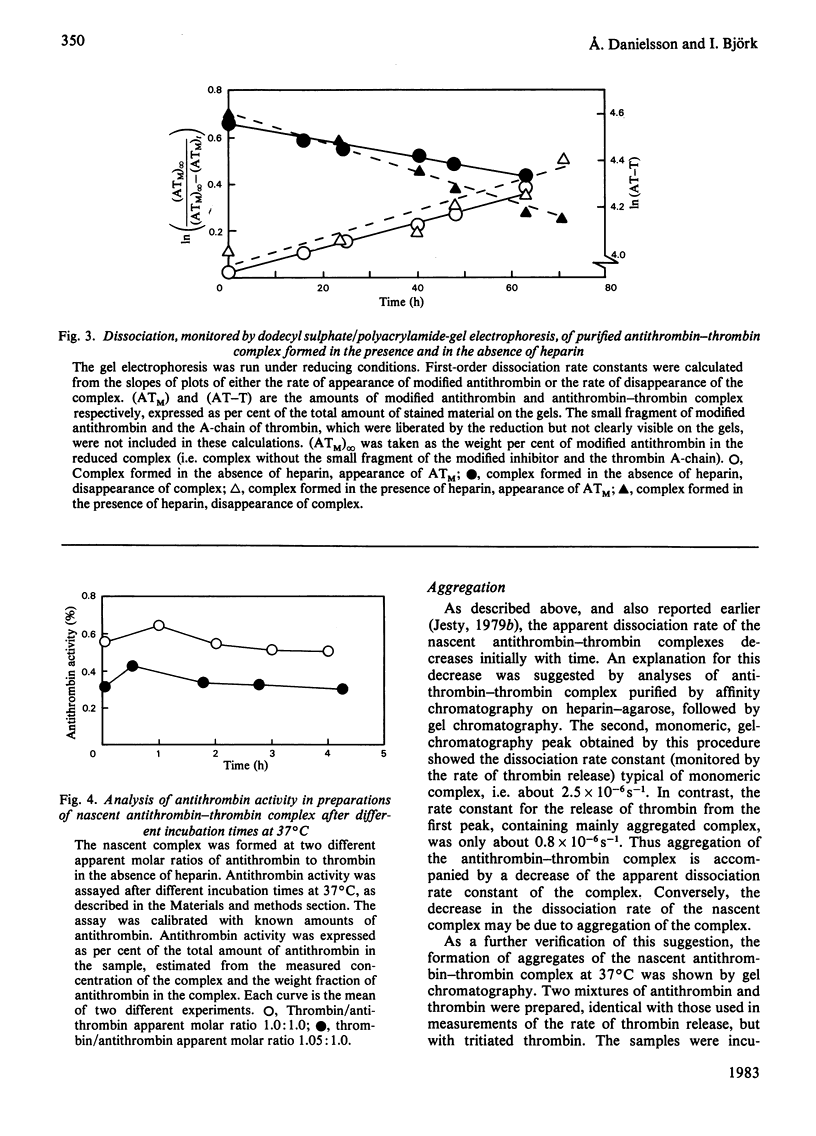
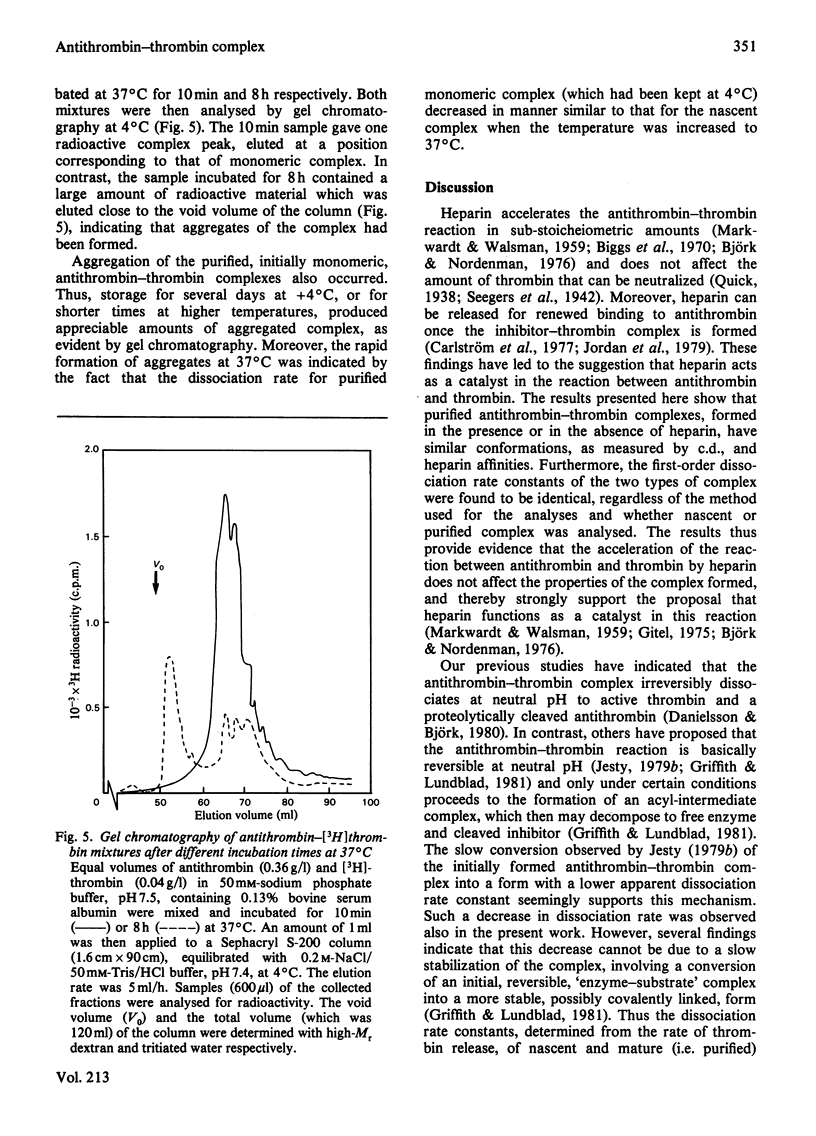
Purification of antithrombin-thrombin complex by ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-agarose resulted in predominantly monomeric complex, whereas purification on matrix-linked heparin produced large amounts of aggregated complex. Monomeric antithrombin-thrombin complexes formed in the presence and in the absence of heparin had similar conformations and heparin affinities. Moreover, the first-order dissociation rate constants, measured by thrombin release, of these complexes were similar, 2.3 X 10(-6)-3.4 X 10(-6)S-1, regardless of whether newly formed or purified complex was analysed. Similar dissociation rate constants were also obtained for purified complex formed with or without heparin, from analyses by dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of the release of modified antithrombin, cleaved at the reactive-site bond. No dissociation of intact antithrombin from the complex was detected by activity measurements or by gel electrophoresis. Aggregation of the complex was found to be accompanied by a decrease in apparent dissociation rate. The similar properties of antithrombin-thrombin complexes formed with or without heparin support the concept of a catalytic role for the polysaccharide in the antithrombin-thrombin reaction. Furthermore, the results indicate that the reaction between enzyme and inhibitor involves the rapid formation of an irreversible, kinetically stable, complex that dissociates into active thrombin and modified, inactive, antithrombin by a first-order process with a half-life of about 3 days. The inhibition thus resembles a normal proteolytic reaction, one intermediate step of which is very slow.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrowcliffe T. W., Johnson E. A., Thomas D. Antithrombin III and heparin. Br Med Bull. 1978 May;34(2):143–150. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler D., Rosenberg R., Jordan R. Fractionation of low molecular weight heparin species and their interaction with antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2902–2913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs R., Denson K. W., Akman N., Borrett R., Hadden M. Antithrombin 3, antifactor Xa and heparin. Br J Haematol. 1970 Sep;19(3):283–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Danielsson A., Fenton J. W., Jörnvall The site in human antithrombin for functional proteolytic cleavage by human thrombin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Jackson C. M., Jörnvall H., Lavine K. K., Nordling K., Salsgiver W. J. The active site of antithrombin. Release of the same proteolytically cleaved form of the inhibitor from complexes with factor IXa, factor Xa, and thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2406–2411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Lindahl U. Mechanism of the anticoagulant action of heparin. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Oct 29;48(3):161–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00421226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Nordenman B. Acceleration of the reaction between thrombin and antithrombin III by non-stoichiometric amounts of heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):507–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlström A. S., Liedén K., Björk I. Decreased binding of heparin to antithrombin following the interaction between antithrombin and thrombin. Thromb Res. 1977 Dec;11(6):785–797. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenka C. H. Long-column meniscus depletion sedimentation equilibrium technique for the analytical ultracentrifuge. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:24–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson A., Björk I. Binding to antithrombin of heparin fractions with different molecular weights. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1930427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson A., Björk I. Slow, spontaneous dissociation of the antithrombin-thrombin complex produces a proteolytically modified form of the inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson R., Andersson L. O. Binding of heparin to human antithrombin III as studied by measurements of tryptophan fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Björk I. Release of a two-chain form of antithrombin from the antithrombin-thrombin complex. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;101(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Orre K., Björk I. Routes of thrombin action in the production of proteolytically modified, secondary forms of antithrombin-thrombin complex. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;101(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J. Kinetics of the heparin-enhanced antithrombin III/thrombin reaction. Evidence for a template model for the mechanism of action of heparin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7360–7365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J., Lundblad R. L. Dissociation of antithrombin III--thrombin complex. Formation of active and inactive antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):105–110. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer E., Kurachi K., Söderström G. The molecular-weight dependence of the rate-enhancing effect of heparin on the inhibition of thrombin, factor Xa, factor IXa, factor XIa, factor XIIa and kallikrein by antithrombin. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):395–400. doi: 10.1042/bj1930395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Björk I., Hopwood J., Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activity of heparin: separation of high-activity and low-activity heparin species by affinity chromatography on immobilized antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J. Dissociation of complexes and their derivatives formed during inhibition of bovine thrombin and activated factor X by antithrombin III. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1044–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J. The kinetics of formation and dissociation of the bovine thrombin.antithrombin III complex. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10044–10050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The binding of low molecular weight heparin to hemostatic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10073–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Fish W. W., Björk I. The thrombin cleavage site in bovine antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80532-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDAHL U., CIFONELLI J. A., LINDAHL B., RODEN L. THE ROLE OF SERINE IN THE LINKAGE OF HEPARIN TO PROTEIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2817–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Tengblad A., Thunberg L., Hök M., Lindahl U. The molecular-weight-dependence of the anti-coagulant activity of heparin. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):691–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1750691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longas M. O., Finlay T. H. The covalent nature of the human antithrombin III--thrombin bond. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):481–489. doi: 10.1042/bj1890481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKWARDT F., WALSMANN P. [Investigations on the mechanism of the antithrombin effect of heparin]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959;317:64–77. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1959.317.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Björk I. Binding of low-affinity and high-affinity heparin to antithrombin. Ultraviolet difference spectroscopy and circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3339–3344. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Björk I. Studies on the binding of heparin to prothrombin and thrombin and the effect of heparin-binding on thrombin activity. Thromb Res. 1978 May;12(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Nyström C., Björk I. The size and shape of human and bovine antithrombin III. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Shore J. D. Binding of high affinity heparin to antithrombin III. Characterization of the protein fluorescence enhancement. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11065–11072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Shore J. D. Demonstration of a two-step reaction mechanism for inhibition of alpha-thrombin by antithrombin III and identification of the step affected by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14891–14895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Multiple functional domains of the heparin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):829–833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. I. Characterization of the reaction products formed during the activation of bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):594–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G. Evidence for the formation of an ester between thrombin and heparin cofactor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper D. S., Banhegyi D., Cash J. D. The different forms of antithrombin II in serum. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Aug 31;38(2):494–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D. Biologic actions of heparin. Semin Hematol. 1977 Oct;14(4):427–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D. Chemistry of the hemostatic mechanism and its relationship to the action of heparin. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., Warner E. D., Brinkhous K. M., Smith H. P. HEPARIN AND THE ANTITHROMBIC ACTIVITY OF PLASMA. Science. 1942 Sep 25;96(2491):300–301. doi: 10.1126/science.96.2491.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten L., Ashwell G. Studies on the chemical and enzymatic modification of glycoproteins. A general method for the tritiation of sialic acid-containing glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1889–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaneuva G. B., Danishefsky I. Evidence for a heparin-induced conformational change on antithrombin III. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):803–809. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallgren P., Nordling K., Björk I. Immunological evidence for a proteolytic cleavage at the active site of antithrombin in the mechanism of inhibition of coagulation serine proteases. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):493–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


