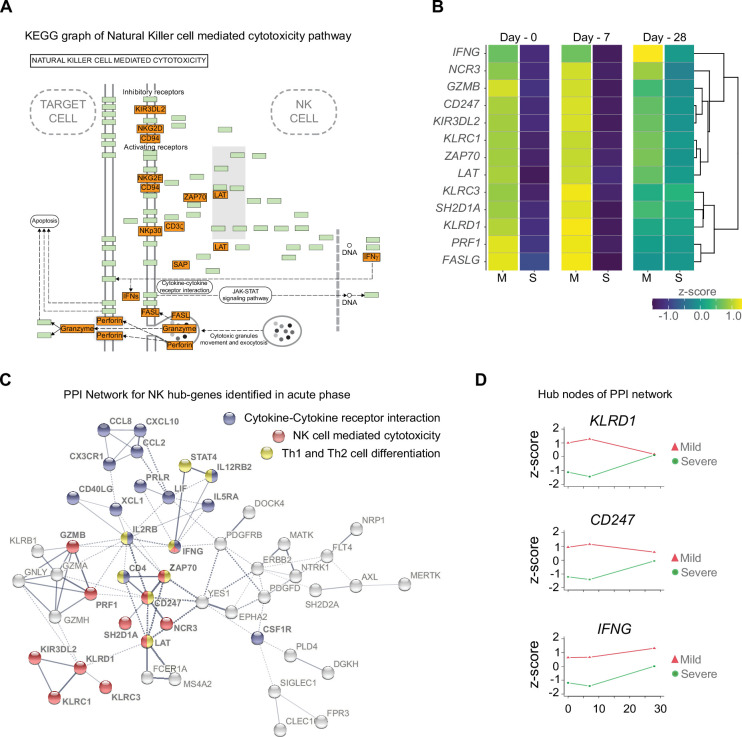
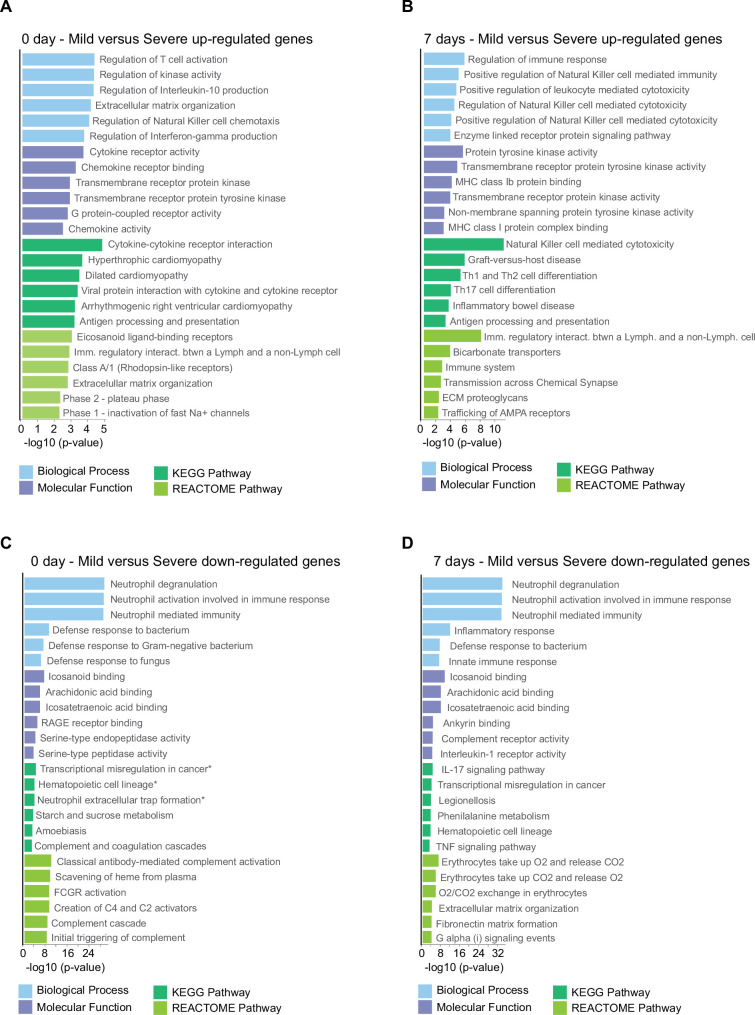
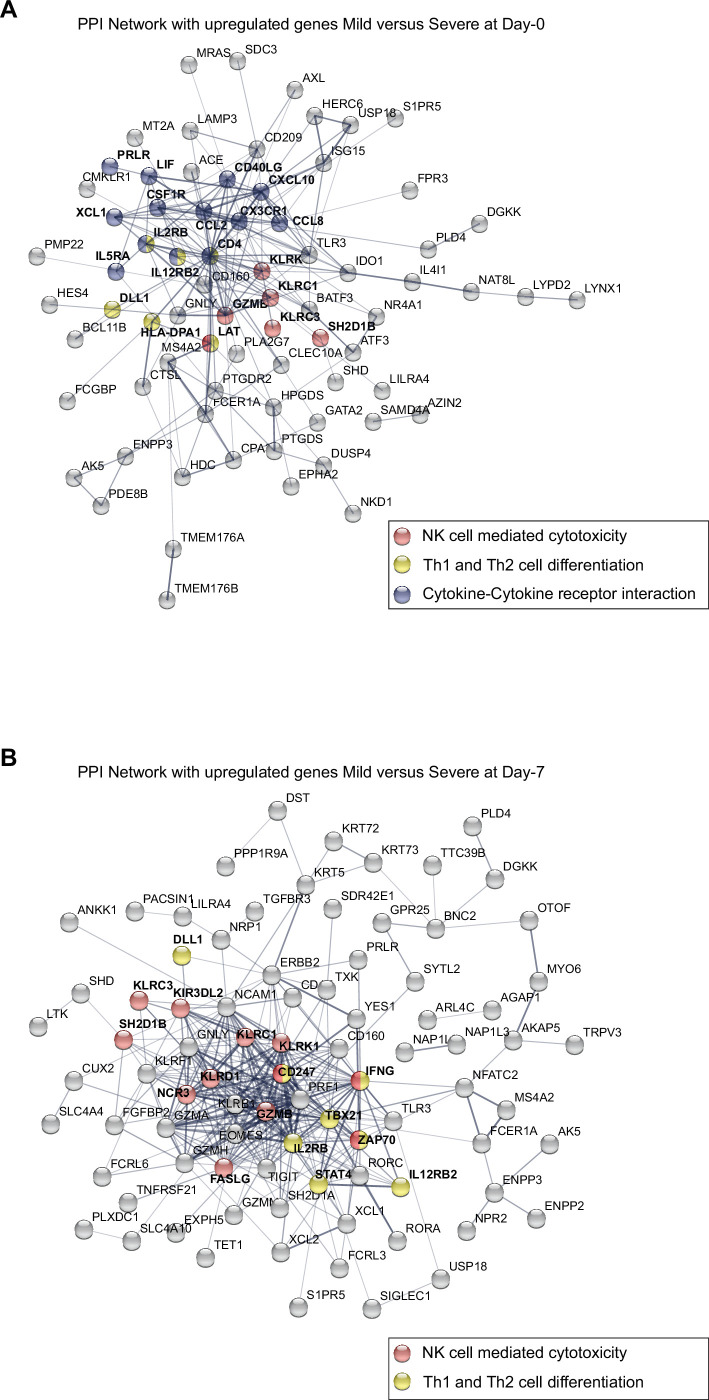
Figure 4. Gene function network for natural killer (NK) cell hub-genes with differential expression levels between mild and severe patients during acute phase of COVID-19.
(A) Kyoto encyclopedia of gene and genomes (KEGG) pathway of NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity represents the set NK cell hub-genes upregulated (red-boxes) in mild versus severe patients. The green boxes correspond to genes without differential expression. (B) Heatmap shows the differential expression levels of NK cell hub-genes over time (D0, D7, and D28 after recruitment) separated by mild and severe groups. The expression levels are represented by the z-score of normalized counts. Dendrogram shows the hierarchical clustering of genes. (C) Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network for upregulated genes during the acute phase in mild patients. The network corresponds to the principal clusters with more interaction between proteins and highlights the three most represented pathways: Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction (blue); NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity (red); and Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation (yellow). (D) Time course expression levels for the main protein nodes identified in PPI network during the acute phase of COVID-19. The trajectories of these genes are graphed as days after recruitment (D0, D7, and D28) for mild (red triangle) and severe (green circle) groups and their enrichment is represented by the z-score of normalized counts.