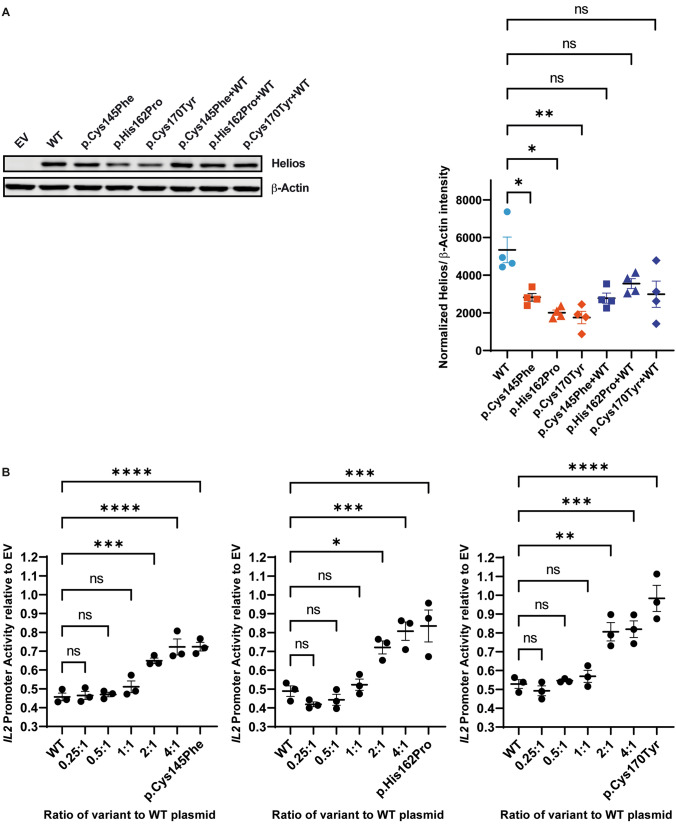
Fig. 6.
Functional evaluation of the identified IKZF2 variants. Variant c.485A>C p.(His162Pro) in family W16-0482, variant c.509G>A p.(Cys170Tyr) in family W22-1907 and variant c.434G>T p.(Cys145Phe) in family W22-2757. A Assessment of variant protein expression in HEK293 cells. Immunoblot analysis of cells transfected with plasmids coding for 3xFLAG-tagged WT Helios or Helios with the amino acid substitutions alone, or a combination of WT and variant plasmids. There is a statistically significant decrease in Helios protein levels when the variants are expressed alone but no significant decrease when the Helios variants are co-expressed with WT Helios (right panel). A parametric one-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. B Luciferase reporter assays to assess the variants’ ability to repress IL2 promotor activity, demonstrating statistically significant decrease in repression of the IL2 promotor by the variant Helios proteins when expressed alone. Upon co-expression of WT and variant Helios in increasing ratios of transfected variant plasmids, a statistically significant decrease of IL2 promoter repression is only observed for ratios of 2:1 and higher. A parametric one-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. EV, empty vector control; IL2, interleukin-2; ns, not statistically significant; WT, wildtype