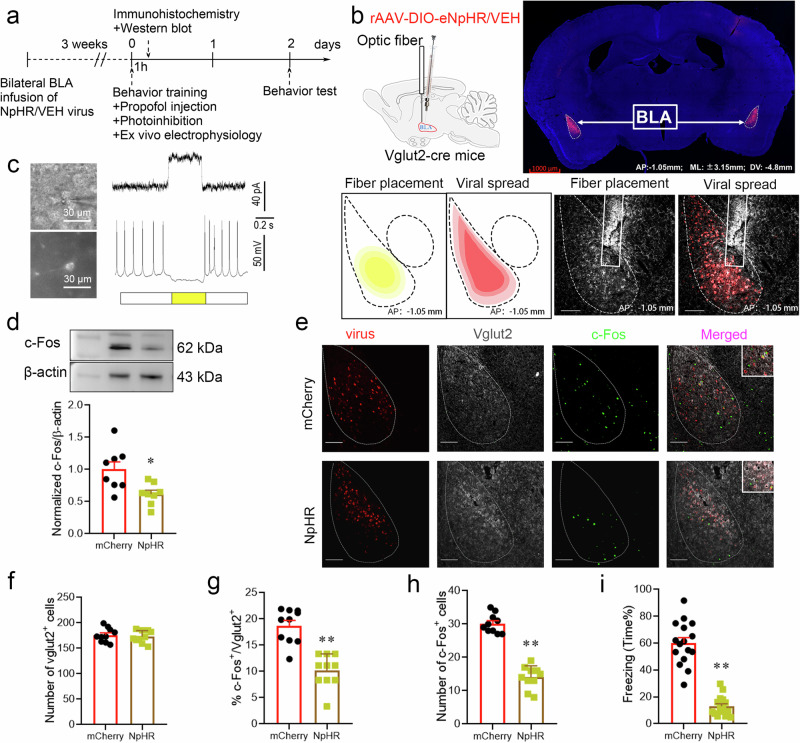
Fig. 4. Inhibiting glutamatergic neurons in the BLA by optogenetic regulation attenuated the enhanced effect of propofol on fear memory.
a Experimental time course for surgery, FC training, propofol injection, photoinhibition, and FCT. b Schematic of 2/9rAAV-DIO-eNpHR-mCherry or 2/9rAAV-DIO-mCherry injection and optic fiber implantation into the BLA of Vglut2-cre mice; representative immunohistochemical staining (scale bar, 1000 µm, AP: -1.05 mm, ML: ±3.15 mm, DV: 4.8 mm); schematic of fiber placement and viral spread in the BLA (scale bar, 100 µm, AP: -1.05 mm). c Neurons expressing mCherry fluorescence were observed in the BLA when ex vivo brain slices were exposed under a microscope. The pulse train evokes outward currents and abolishes action potentials (30 pA) in glutamatergic neurons. d Representative Western blot image and quantification of c-Fos expression. The expression of c-Fos was reduced after the photoinhibition of glutamatergic neurons in the BLA (n = 8, two-tailed unpaired t test, *p = 0.012). e Representative images of mCherry/Vglut2/c-Fos immunofluorescence in BLA neurons after virus treatment and photoinhibition; scale bar, 100 µm. f–h The ratio of c-Fos+ & Vglut2+ cells and the total number of c-Fos+ cells in the BLA after the photoinhibition of glutamatergic neurons were reduced (n = 10/group, two-tailed unpaired t test, **p < 0.01). i Reduction in freezing in mice after the photoinhibition of glutamatergic neurons in the BLA (n = 16/group, two-tailed unpaired t test, **p < 0.01). All data are presented as the mean ± SEM.