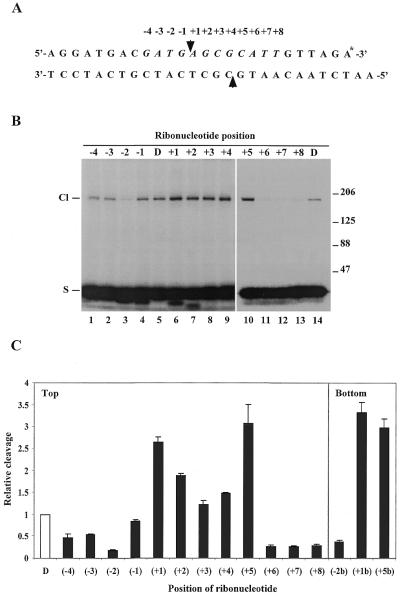
Figure 1.
Position-specific effect of ribonucleotides on human topoisomerase II-mediated cleavage. (A) Schematic illustration of the topoisomerase II cleavage substrate. The arrowheads represent the points of topoisomerase II-mediated cleavage. A single ribonucleotide was incorporated into the top strand of the substrate at different positions ranging from –4 to +8 relative to the cleavage site as indicated above the sequence. The asterisk at the 3′-end of the top strand illustrates radioactive labelling. (B) Human topoisomerase IIα-mediated cleavage of the ribonucleotide-containing substrates. Cleavage was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The SDS-stopped samples were loaded directly on an 8% SDS–polyacrylamide gel and cleavage complex formation was visualized after autoradiography due to covalent linkage of the protein to the labelled top strand. The position of the ribonucleotide in the substrate is as indicated above the lanes. D represents the control DNA substrate. Cl and S indicate the positions of the protein-linked cleavage complex and the cleavage substrate, respectively. The numbers to the right of the gel illustrate the sizes of protein markers in kDa. (C) Schematic presentation of the positional effect of ribonucleotides on human topoisomerase IIα-mediated cleavage. Cleavage experiments were performed as described in (B) using substrates containing a single ribonucleotide located at different positions ranging from –4 to +8 in the top strand or at the –2, +1 or +5 position in the bottom strand, as indicated below the histogram. In all cases cleavage was measured on the top strand. Cleavage levels were determined after PhosphorImager scanning of the gels and are presented relative to the cleavage level obtained with the control DNA substrate. Data represent the averages of three independent experiments and standard deviations are indicated by error bars.