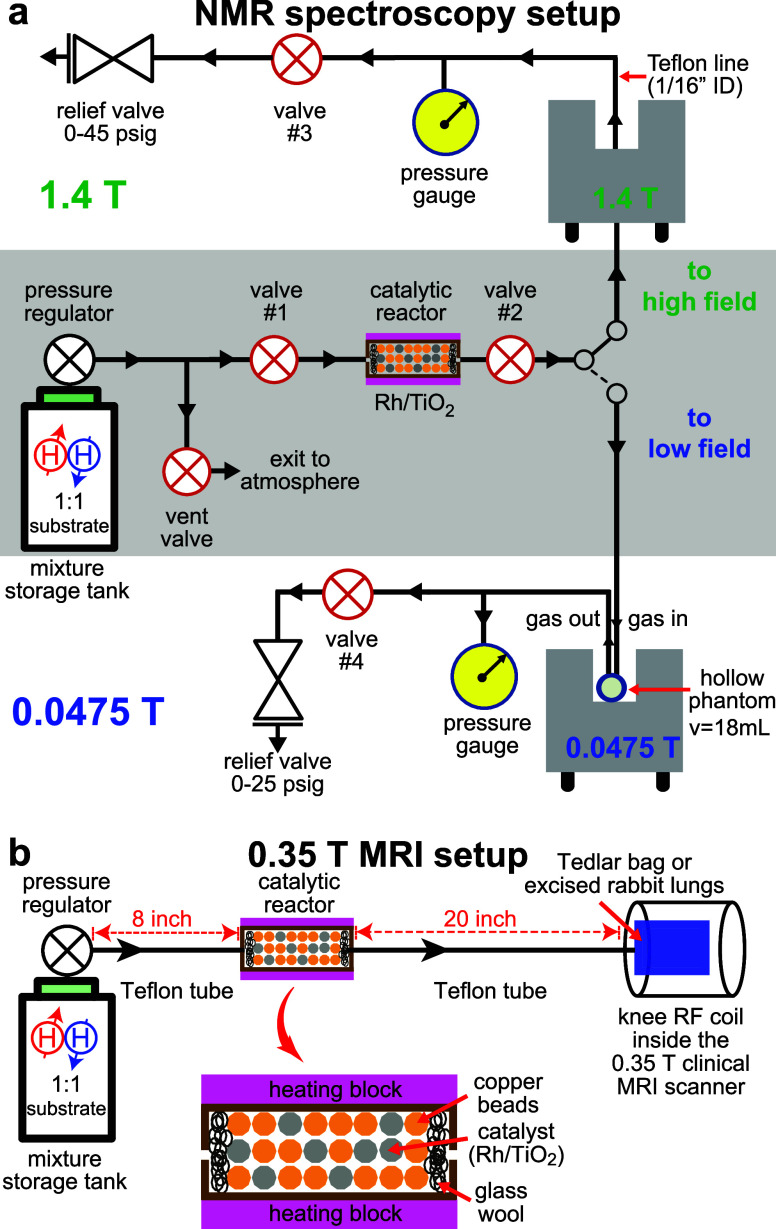
Figure 1.
(a) Experimental setup for heterogeneous pairwise p-H2 addition to unsaturated substrate molecules (propene, 1-butene, or 2-butene). The storage gas tank contained a 1:1 gas mixture of p-H2 and the unsaturated precursor that is directed through the reactor (heated to 150 °C) using manual valves. HP product gas exits the reactor, and it is directed to the NMR detector (with the gas being detected inside a 1/16-in.-ID Teflon line at 1.4 T or inside a hollow plastic spherical phantom when using the 0.0475 T magnet). The estimated flow rate of the HP gas was 6–8 sLm. (b) MRI experimental polarizer setup used for clinical-scale imaging. A portable gas-mixing storage tank is connected to the high-flow catalytic reactor (estimated flow rate is 30–40 sLm). The HP gas exits the reactor and inflates the Tedlar bag situated in the knee RF coil of a 0.35 T clinical MRI scanner (see the main text describing the setup modification for HP gas injection inside the excised rabbit lungs). Parahydrogen addition was performed at the Earth’s magnetic field.