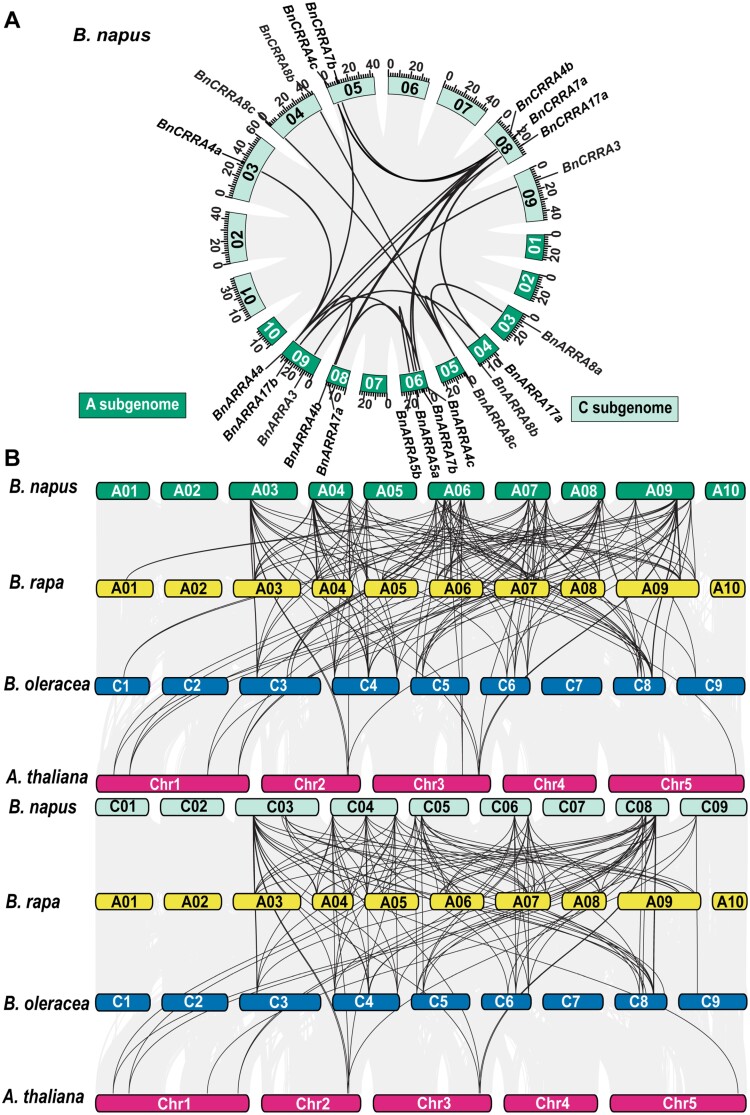
Fig. 4.
The syntenic conservation of B. napus RRA genes. (A) Synteny of the BnRRA genes. Gray lines represent syntenic blocks in the B. napus genome, while black lines indicate paralogous BnRRA gene pairs, demonstrating segmental duplication between different chromosomes. The A and C subgenomes are distinguished by the color difference in the box bearing the chromosome name. The scale at the bottom of these boxes represents the size of the chromosome in megabases. (B) Collinearity of B. napus (A and C subgenome), B. rapa, B. oleracea, and A. thaliana genomes. Gray lines illustrate collinear blocks among these species, while black lines show the orthology in the BnRRA, BrRRA, BoRRA, and A. thaliana RR genes. The dark and light green boxes represent the chromosomes in the A and C subgenomes of B. napus, the yellow boxes for the B. rapa chromosomes, the blue boxes for the B. oleracea chromosomes, and the dark pink boxes for the A. thaliana chromosomes (designated as ‘Chr’).