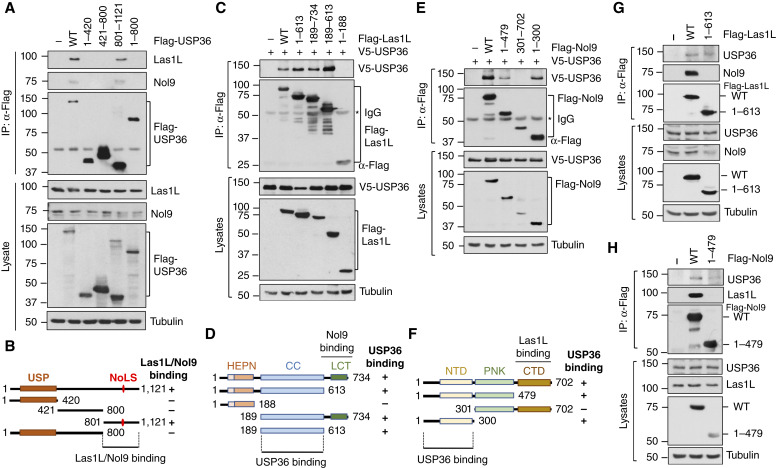
Figure 2.
Mapping the interaction of USP36 with the Las1L–Nol9 complex. A and B, The C-terminal domain of USP36 binds to Las1L and Nol9. H1299 cells transfected with Flag-USP36 or its deletion mutants were assayed by Co-IP with anti-Flag antibody, followed by IB (A). Diagram of USP36 indicating the C-terminal Las1L–Nol9–binding domain is shown in B. USP, ubiquitin-specific protease. C and D, USP36 binds to the CC domain of Las1L. H1299 cells transfected with Flag-Las1L or its deletion mutants together with V5-USP36 were subjected to Co-IP with anti-Flag antibody, followed by IB (C). The diagram of Las1L domains is shown in D. HEPN, higher eukaryotes and prokaryotes nucleotide-binding domain; LCT, Las1L C-terminal tail; CC, coiled-coil. E and F, USP36 binds to the NTD domain of Nol9. H1299 cells transfected with Flag-Nol9 or its deletion mutants together with V5-USP36 were subjected to Co-IP with anti-Flag antibody, followed by IB (E). The diagram of Nol9 domains is shown in F. NTD, N-terminal domain; PNK, polynucleotide kinase; CTD, C-terminal domain. G and H, USP36 binds to Las1L and Nol9 independently. H1299 cells transfected with WT Flag-Las1L or the Nol9-binding defective mutant (G) or Flag-Nol9 or its Las1L-binding defective mutant (H) were subjected to Co-IP with anti-Flag antibody, followed by IB.