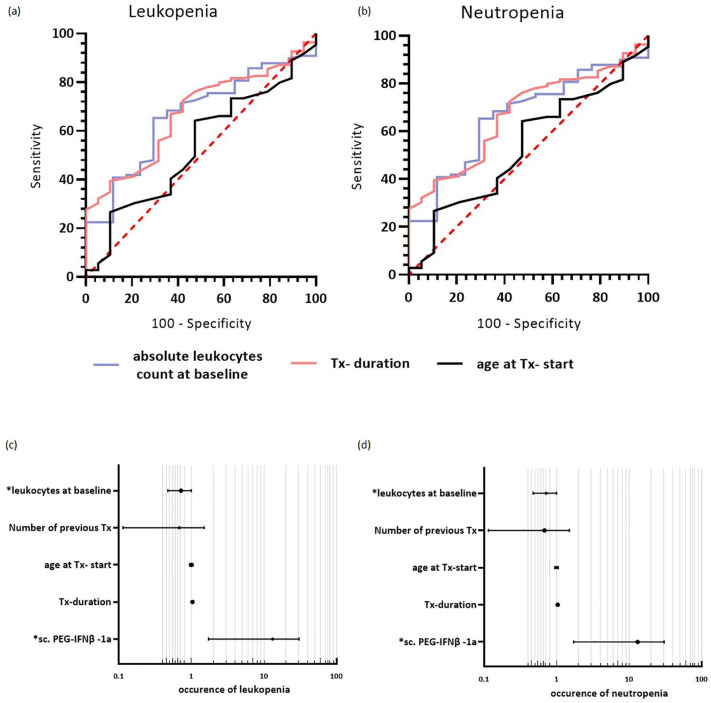
Figure 3.
Predictive factors for the incidence of leukopenia and neutropenia. (a and b) ROC curve—predicting the occurrence of (a) leukopenia and (b) neutropenia in the whole cohort. (a) Leukocytes at baseline (AUC: 0.751, 95% CI: 0.648–0.854, p < 0.001, cut-off value of ⩽6.99 leukocytes/nl (Youden-Index)) was identified as a significant risk for leukopenia; treatment duration and age at treatment were not significant (treatment duration: AUC = 0.588, 95% CI: 0.497–0.674, p = 0.149; age at treatment start: AUC = 0.500, 95% CI: 0.388–0.612, p = 0.997 ). (b) Regarding the occurrence of neutropenia, leukocytes at baseline (AUC = 0.664, 95% CI: 0.540–0.787, p = 0.032, cut-off value for leukocytes at baseline ⩽6.55 leukocytes/nl (Youden-Index)) and treatment duration with interferons (AUC = 0.312, 95% CI: 0.199–0.425, p = 0.013, treatment duration >27 months (Youden-Index)), significantly identify patients developing neutropenia; age at treatment initiation was not significant. (c and d) Forest plots showing the determined OR for the occurrence of (c) leukopenia and (d) neutropenia. The binary logistic regression model revealed “use of sc. PEG-IFN-β-1a” and “leukocyte count at baseline” as significant predictors for the dependent variable “occurrence of leukopenia” under IFN therapy; “use of sc. PEG-IFN-β-1a” and “leukocyte count at baseline” were significant predictors for the dependent variable “occurrence of neutropenia” under IFN therapy.
AUC, area under the curve; CI, 95% confidence interval; IFN-β, interferon-beta; OR, odds ratio; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; sc., subcutaneous; Tx, drug treatment.