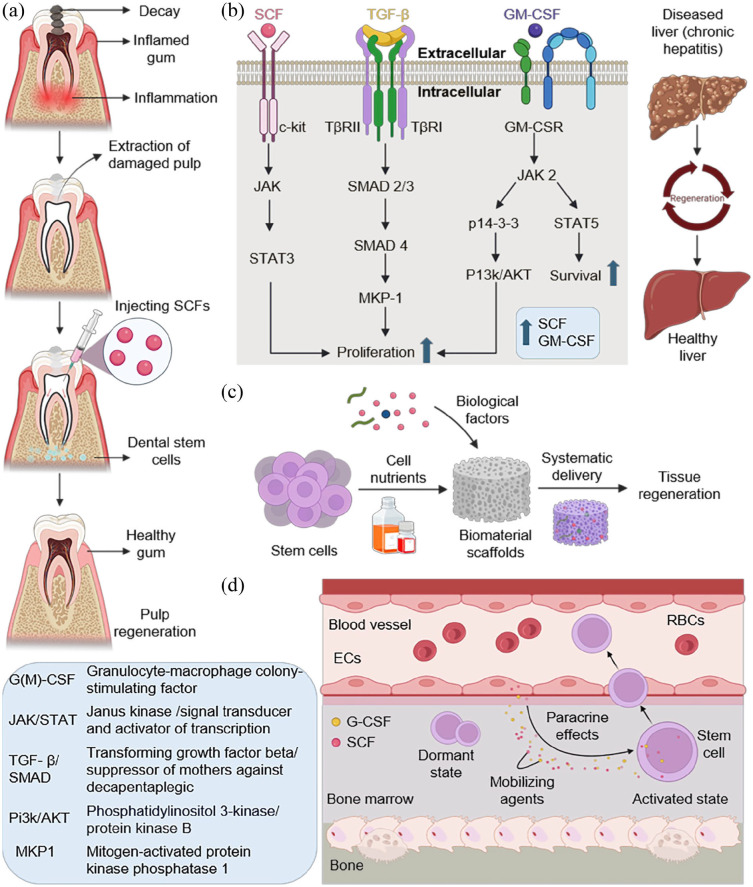
Figure 3.
The role of SCF in regeneration. (a) SCFs are administered into the pulp using a syringe after cleaning damaged tooth areas. The interaction between dental stem cells and SCF helps in the regeneration of dental pulp. (b) Mechanism for the regeneration of liver tissue. The combined effect of SCF, TGF-β and GM-CSF with their respective signaling pathways facilitates the liver cell proliferation and survival, which aid in inducing liver regeneration. (c) SCF facilitates the construction of scaffolds as a basis for tissue regeneration. The cocktail of stem cells and biological growth factors are introduced separately into the biomaterials of choice. Cocktail laden biomaterials are implanted symmetrically in vivo, enhancing tissue regeneration. (d) The paracrine effects of SCFs exerted on stem cells for activation and mobilization into blood circulation from BM. SCFs and G-CSF secreted by ECs act as mobilizing agents that activate dormant stem cells. The activated stem cells trespass into blood vessel form bone microenvironment.