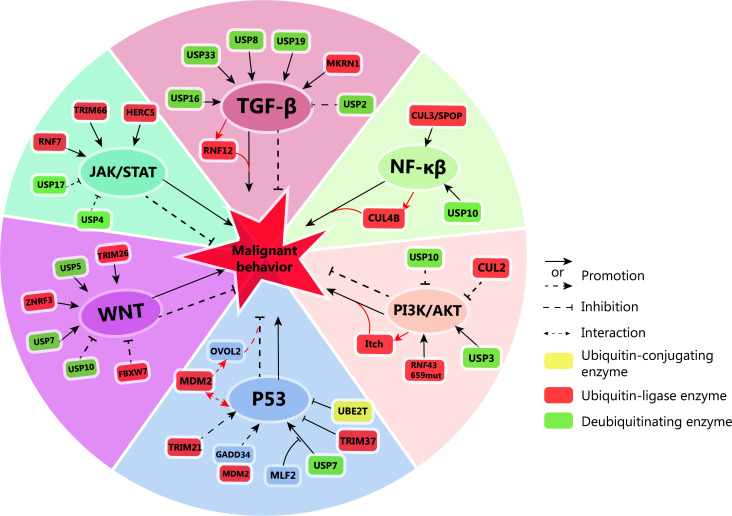
Figure 2.
Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of key signaling pathways in tumor cells. Ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases have pivotal roles in modulating the activation or inhibition of TGF-β, NF-κβ, WNT, PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT, and P53 signaling pathways in tumor cells. These pathways, in turn, influence the malignant behavior of tumors. Notably, the activation of some signaling pathways can also lead to the activation of downstream ubiquitin ligases, further impacting tumor progression. TGF-β: deubiquitinases ubiquitin-specific protease 16 (USP16), USP33, USP8, USP19, and the makorin ring finger protein 1 (MKRN1) activate the TGF-β signaling pathway. The activation of TGF-β further activates ring finger protein 12 (RNF12). These events collectively contribute to the malignant behavior of tumors. Conversely, USP2 inhibits TGF-β signaling, suppressing tumor growth. NF-κβ: USP10 and cullin-3/ speckle-type POZ protein (CUL3/SPOP) activate the NF-κβ signaling pathway, promoting tumor formation. NF-κβ activation also upregulates CUL4B, further driving tumor growth. WNT: USP7, USP5, and zinc and ring finger 3 (ZNRF3), tripartite motif containing 26 (TRIM26) activate the WNT pathway, promoting tumorigenesis. Conversely, USP10 and recombinant F-box and WD repeat domain containing protein 7 (FBXW7) inhibit tumorigenesis by suppressing the WNT pathway. PI3K/AKT: RNF43 and USP3 activate the PI3K/AKT pathway, promoting tumorigenesis. Conversely, CUL2 and USP10 inhibit PI3K/AKT, suppressing tumorigenesis. Activated PI3K/AKT can further activate ubiquitin ligase Itch, contributing to tumorigenesis. JAK/STAT: RNF7, TRIM66, and HERC5 activate the JAK/STAT pathway, promoting tumorigenesis. USP17 and USP4 inhibit the JAK/STAT pathway, suppressing tumorigenesis. p53: TRIM21 activates the p53 pathway, while growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible gene 34 (GADD34) competitively binds to mousedouble minute 2 (MDM2) to promote p53 expression. These events collectively inhibit tumorigenesis. TRIM37 and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (UBE2T) inhibit p53 expression, while myeloid leukemia factor 2 (MLF2) inhibits the binding of USP7 to p53, further promoting tumorigenesis. Additionally, p53 interacts with MDM2, which in turn promotes the expression of OVO-like zinc finger 2 (OVOL2) and inhibits tumorigenesis.