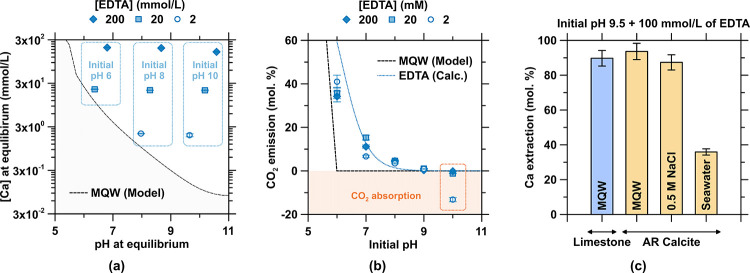
Figure 3.
Dissolution of calcite at room temperature in the presence of EDTA. (a) Increased solubility of calcite (i.e., Ca concentration) as a function of the pH across a range of EDTA concentrations. The black dashed line shows the thermodynamically modeled solubility of calcite in a system devoid of EDTA. (b) Degassing of CO2 expressed as a molar percentage of total amount of aqueous and mineralized carbonates in the system as a function of the EDTA concentration and the initial pH of the solution. The dashed black line shows the thermodynamically modeled CO2 emission from calcite in a system devoid of EDTA, and the blue dotted line shows the CO2 emission of calcite in a system containing EDTA calculated using eqs 12–14. (c) Ca concentration at equilibrium at pH 9.5 and in the presence of 100 mmol/L EDTA in MQW, a 0.5 mol/L NaCl solution, and simulated seawater (“Instant Ocean Seawater: IOSw”) for reagent calcite (AR calcite) or limestone rock.