Fig. 2. Cancer-related survival in patients with GS-intestinal, GS-diffuse, CIN-intestinal, and CIN-diffuse tumors.
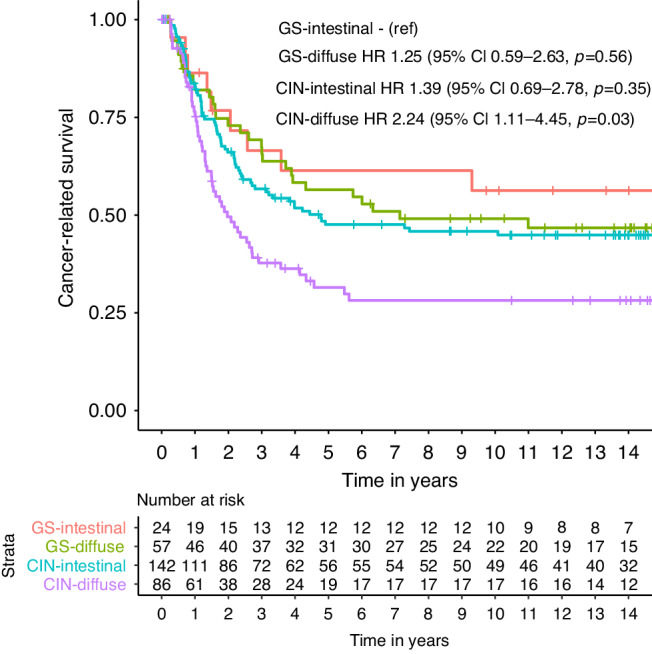
Differences in cancer-related survival were assessed using the Kaplan–Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. The hazard ratio was 1.25 (95% CI 0.59–2.63, p = 0.56) for GS-diffuse, 1.39 (95% CI 0.69–2.78, p = 0.35) for CIN-intestinal, and 2.24 (95% CI 1.11–4.54, p = 0.03) for CIN-diffuse, all compared to GS-intestinal. P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. GS genomically stable, CIN chromosomal instable.
