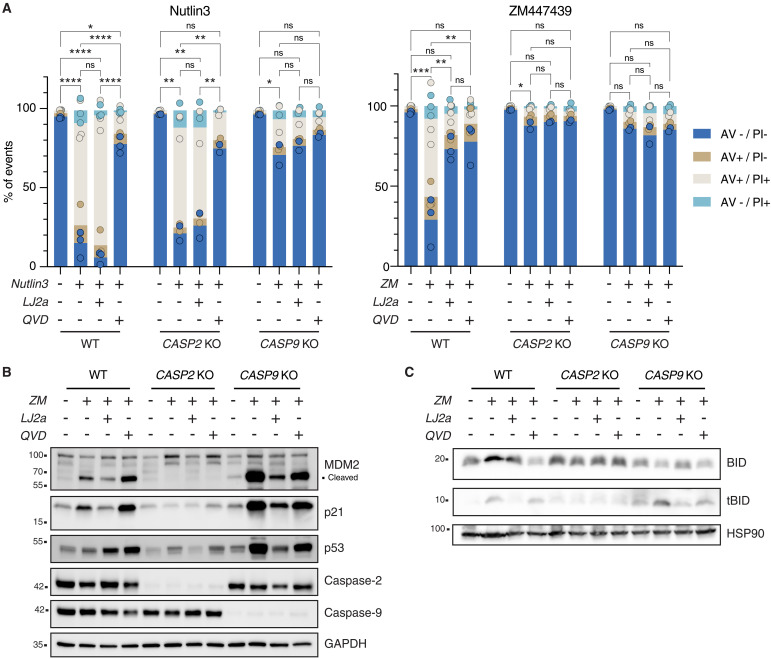
Fig. 4. Chemical caspase-2 inhibition reduces cytokinesis failure–dependent cell death.
(A) Nalm6 WT, caspase-2 KO, and caspase-9 KO cells were treated with 10 μM Nutlin3 or 2 μM ZM alone or in combination with the caspase-2 inhibitor LJ2a (10 μM) or the pan-caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (QVD; 10 μM) or left untreated for 48 hours before staining with annexin V/PI followed by flow cytometric analysis. Bar charts represent the means of the percentage of events in each staining condition, the dots represent the values for each single replicate. Statistical significance was calculated on the percentage of live cells by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple-comparison correction, comparing each condition within the genotype. N ≥ 2 independent biological replicates. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. See also fig. S4. (B) Western blot analysis of Nalm6 WT, caspase-2 KO, and caspase-9 KO cells after 48 hours of treatment with 2 μM ZM, alone or in combination with the caspase-2 inhibitor LJ2a (10 μM) or the pan-caspase inhibitor QVD (10 μM) (or untreated controls). (C) Western blot analysis of Nalm6 cells as described in (B).