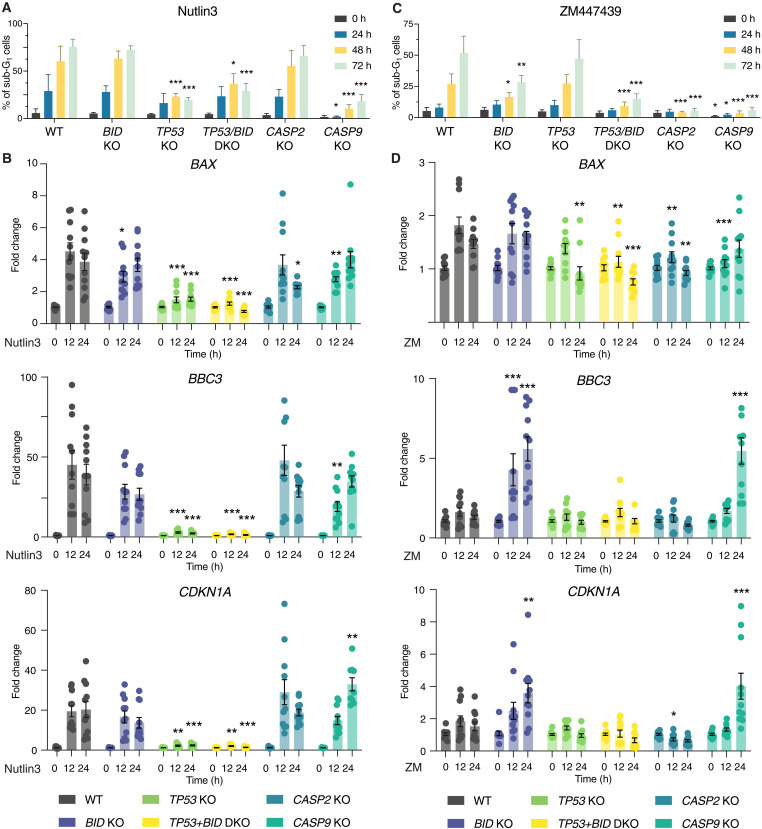
Fig. 6. Loss of BID enables p53-dependent transcription in Nalm6 cells after cytokinesis failure.
(A) Quantification of the percentage of sub-G1 cells of different Nalm6 clones at different time points after 10 μM Nutlin3 treatment. Data are presented as means ± SD of N ≥ 3 independent biological replicates. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison testing, comparing each time point of the KO clones to the corresponding time point of the WT sample. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of the p53 targets BAX, BBC3/PUMA, and CDKN1A/p21 of Nalm6 WT and derivative clones at different time points after 10 μM Nutlin3 treatment. Results are normalized over the housekeeping gene GAPDH and presented as fold change over the time point zero hour for each clone. Data are presented as means ± SEM, and individual points represent the values of N = 4 independent biological replicates. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test, comparing each KO clone to the WT sample at the corresponding time point. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) Same as in (A), but after 2 μM ZM treatment. (D) Same as in (B), but after 2 μM ZM treatment.