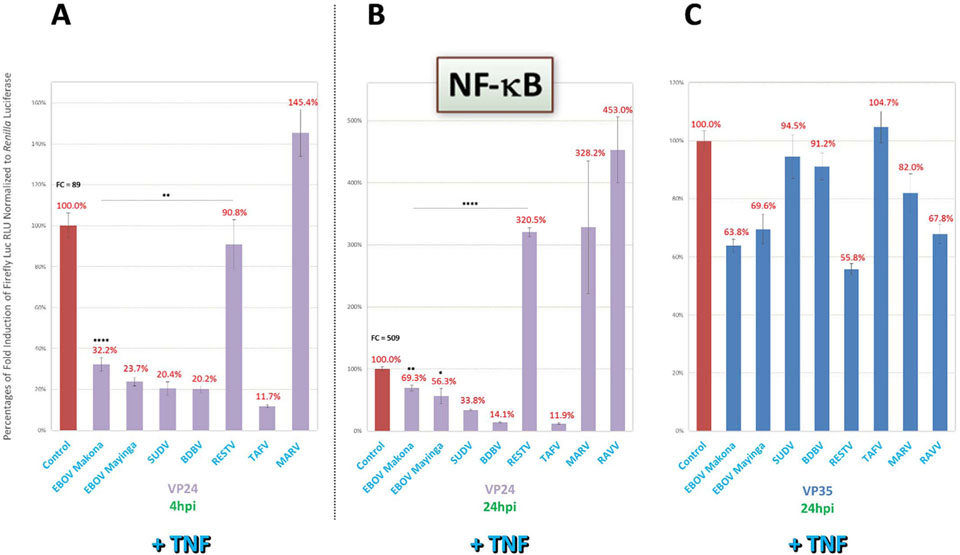
Fig. 8.
VP24 of all ebolaviruses except RESTV also display strong inhibition of early TNF-induced NF-κB activity, and later, virus species-specific variable inhibition, despite prominent loss of VP35 activity. Reporter assays as described in Fig. 2 were conducted to further characterize putative species-specific VP24 antagonism on NF-κB activity. (A–C) Cells cotransfected with NF-κB activity reporter were directly induced 1dpt by TNF (50 ng/mL) and harvested 4hpi (A) or 24hpi (B) to assess VP24 inhibitory activity for early or late TNF receptor-based response activation, respectively, or 24hpi to assess VP35 inhibitory activity (C), as indicated. FC = fold change of positive induction relative to uninduced negative control. RLU = relative light units. *=p < 0.05; **=p < 0.005; ***=p < 0.0005; ****=p < 0.0001; asterisks above horizontal lines indicate direct comparison of activity values between two antagonists.