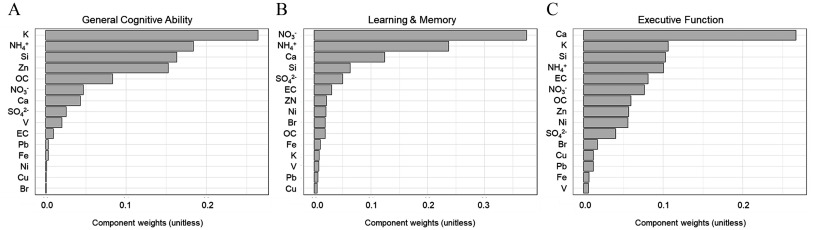
Figure 4.
Individual component weights from the mixture effects on neurocognitive performance in 9- to 10-year-old participants from the ABCD Study cohort () from 2016 to 2018. Bar charts indicate weights of components contributing to the overall WQS mixture index for the three cognitive outcomes: (A) general cognitive ability, (B) learning & memory, and (C) executive function. Results from WQS regression models of the 15 components, adjusting for age, sex, race/ethnicity, overall household income, perceived neighborhood safety, urbanicity, physical activity, and daily screen average hours and site. Note: Br, bromine; Ca, calcium; Cu, copper; EC, elemental carbon; Fe, iron; K, potassium; , ammonium; Ni, nickel; , nitrate; OC, organic carbon; Pb, lead; Si, silicon; , sulfate; V, vanadium; WQS, weighted quantile sum; Zn, zinc. Numeric data for Figure 4 can be found in Excel Tables S4–S6.