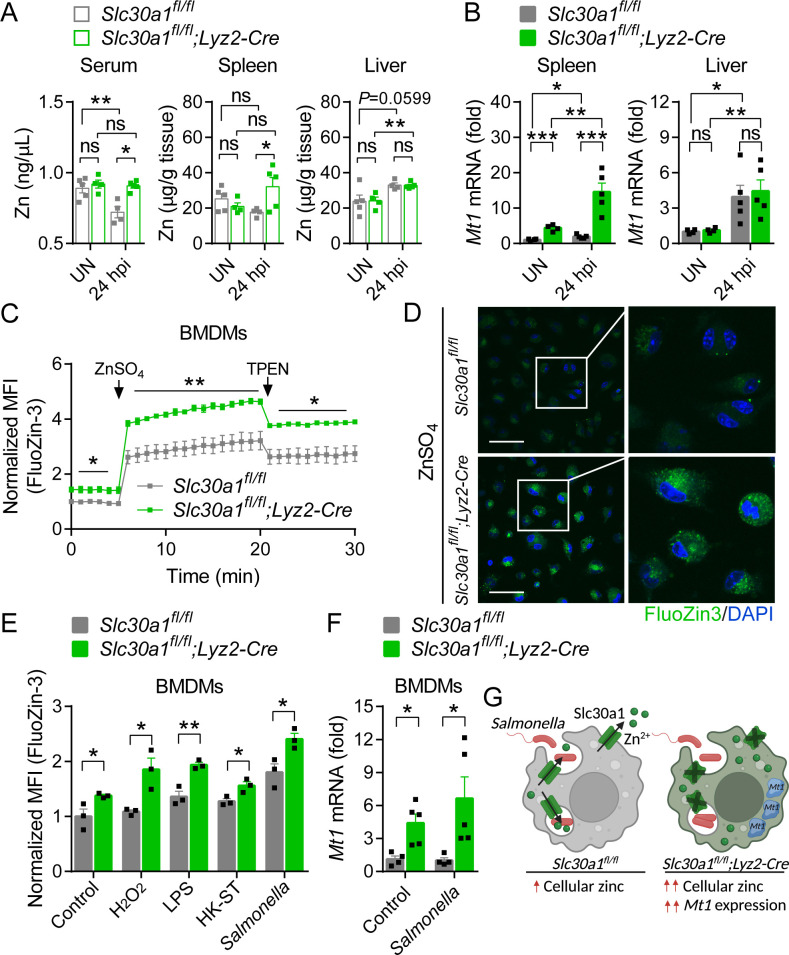
Figure 6. Loss of Slc30a1 in macrophages causes intracellular zinc accumulation.
(A) Summary of zinc (Zn) content measured in the serum, spleen, and liver of uninfected (UN) and Salmonella-infected mice at 24 hpi (n = 4–5 mice/group). (B) RT-qPCR analysis of Mt1 mRNA in the spleen and liver of the indicated mice. (C) Time course of normalized FluoZin-3 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) measured in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs); where indicated, ZnSO4 (100 µM) and N, N,N′,N′-tetrakis-(2-pyridyl-methyl)-ethylenediamine (TPEN) (4 µM) were applied to the cells. (D) Confocal fluorescence images of BMDMs stained with FluoZin-3 (green) after treatment with ZnSO4 for 15 min; the nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 µm. (E) Summary of normalized FluoZin-3 MFI measured in BMDMs 30 min after application of H2O2 (1 mM), lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 µg/ml), heat-killed Salmonella typhimurium (HK-ST) (multiplicity of infection [MOI] = 100), or Salmonella (MOI = 10) (n = 3). (F) RT-qPCR analysis of Mt1 mRNA in uninfected and Salmonella-infected BMDMs (n = 5). (G) Model showing the predicted effects of the loss of Slc30a1 on cellular zinc trafficking and intracellular zinc accumulation in BMDMs in response to Salmonella infection. Data in this figure are represented as mean ± SEM. p values were determined using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ns, not significant.
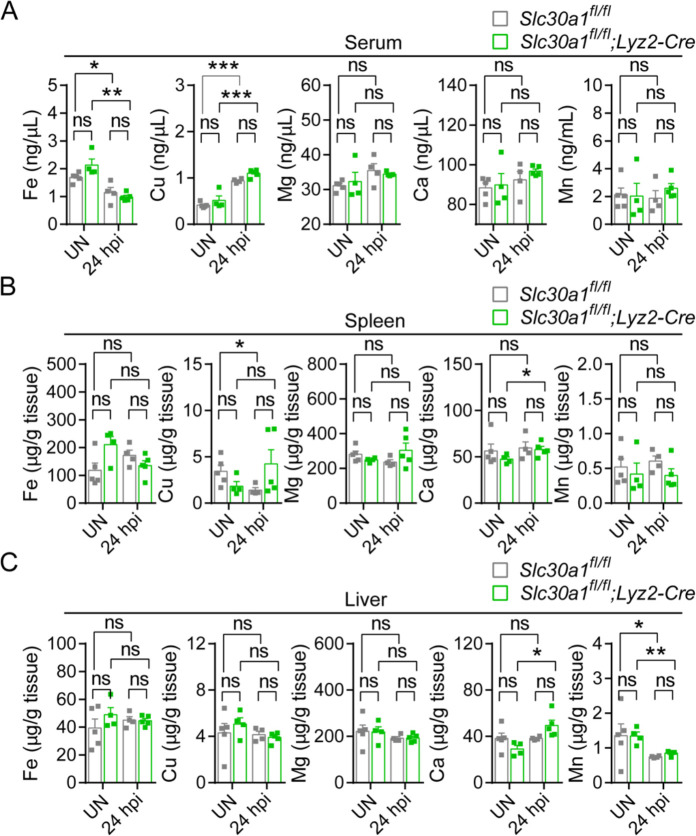
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Except for Zn, Lyz2-Cre-mediated genetic deletion of Slc30a1 in mice does not affect the content of other trace minerals.
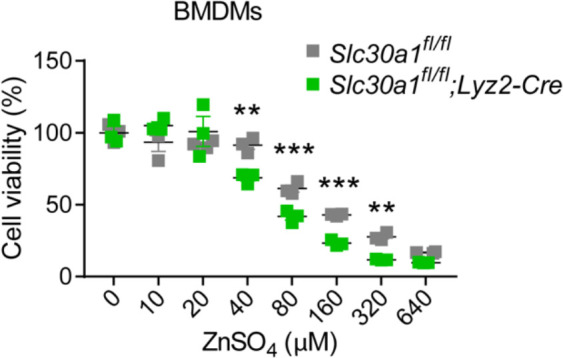
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Slc30a1 deficiency increase sensitivity to zinc stress.