Figure 5.
Complement deposition on S. aureus by WTA glycoprofile-specific IgM is reduced in ICU patients that succumbed to S. aureus bacteremia
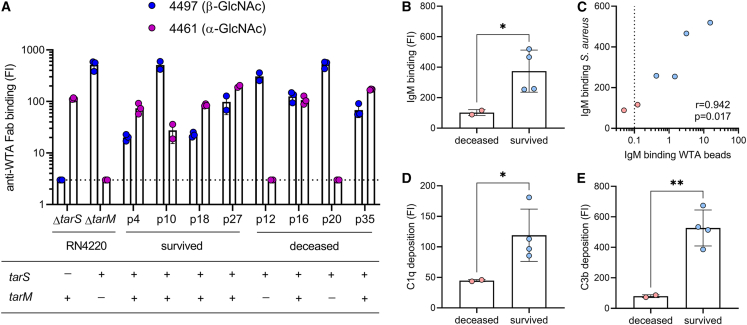
(A) Expression of β-GlcNAc-WTA (Fab clone 4497) and α-GlcNAc-WTA (Fab clone 4461) by clinical isolates from eight patients (survived patients: p4, p10, p18, p27; deceased patients: p12, p16, p20, p35) and reference strains RN4220 ΔtarS and ΔtarM. Below the corresponding WTA glycosyltransferase genotypes (tarS, tarM) as determined by PCR analysis. The dotted line indicates background staining.
(B) IgM binding to S. aureus strain Newman Δspa/sbi in 1% plasma from six patients infected with a tarS+tarM+S. aureus isolate (as shown in A), stratified on ICU mortality.
(C) Spearman correlation between IgM binding to S. aureus (shown in A) and cumulative IgM binding to TarS-WTA and TarM-WTA beads in six patients, with deceased patients shown in red and survived patients in blue. Dotted line represents the lower limit of quantification and symbols shown below the line represent extrapolated values.
(D and E) Deposition of (d) C1q and (e) C3b on Newman Δspa/sbi, pre-opsonized with 3% patient plasma, stratified on ICU mortality. Anti-WTA Fab staining, deposition of IgM, C1q and C3b on S. aureus bacteria is depicted as geometric mean fluorescence intensity (FI) (mean + SD of biological duplicates or triplicates), each symbol indicates individual patients. Statistical analysis for C, D, and E was performed using unpaired t tests with Welch correction. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. See also Figure S6.