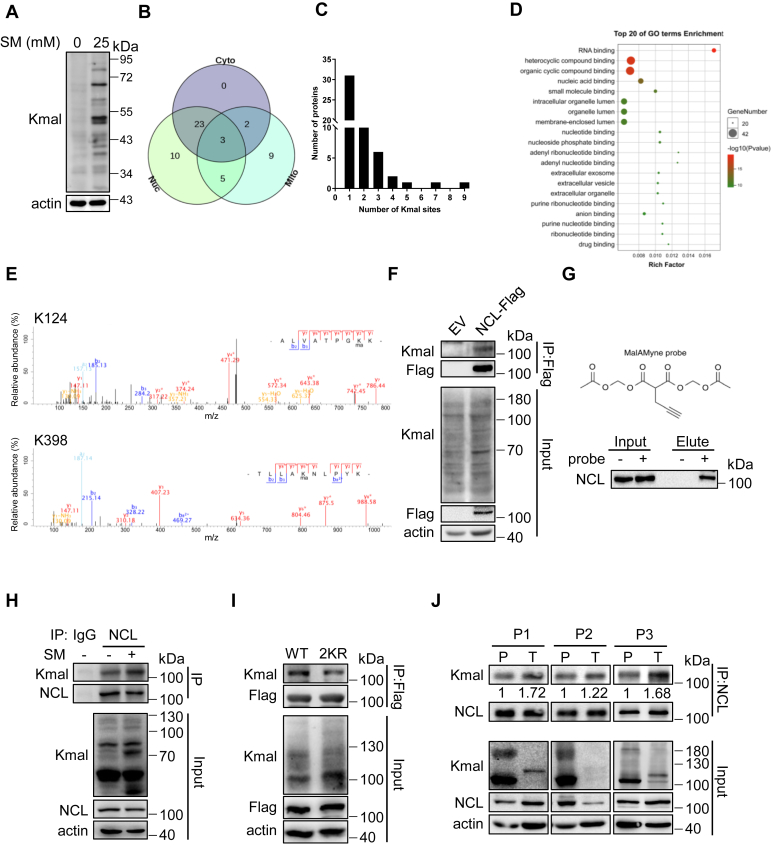
Figure 2.
Nucleolin is malonylated in HCC cells at lysine 124 and 398.A, immunoblotting of Kmal from HepG2 cells treated with 25 mM SM for 72 h. B, Venn diagram displaying the number of Kmal proteins and their subcellular distributions as determined by the COMPARTMENTS database. Cyto indicates cytoplasmic proteins; Mito indicates mitochondrial proteins; Nuc indicates nuclear proteins. C, histogram of the number of Kmal sites per protein. D, results from DAVID gene ontology (GO) analysis showing malonylated proteins categorized by molecular function for visualization. Top 20 pathways were shown. E, the lysine-124 and -398 residues of NCL were identified to be Kmal targeting sites by mass spectrometry. F, immunoprecipitation of Flag from HepG2 cells with stable expression of empty vector (EV) or NCL-Flag. G, HepG2 cells were incubated with MalAM-yne (200 μM) or vehicle control for 2 h, followed by click chemistry to label the probe with biotin. Then, immunoprecipitation was performed using streptavidin beads. Samples were blotted for NCL via immunoblotting. H, immunoprecipitation showing Kmal of endogenous NCL in HepG2 cells with or without sodium malonate treatment (25 mM, 72 h). I, immunoprecipitation showing Kmal of ectopic NCL in HepG2 cells with stable expression of NCL-Flag (WT) or NCL2KR-Flag (2 KR). J, immunoprecipitation showing Kmal of endogenous NCL in HCC and para-HCC biopsy of volunteered patients. Kmal of NCL in each tumor tissue was normalized by the modification level in corresponding paracancerous tissue.