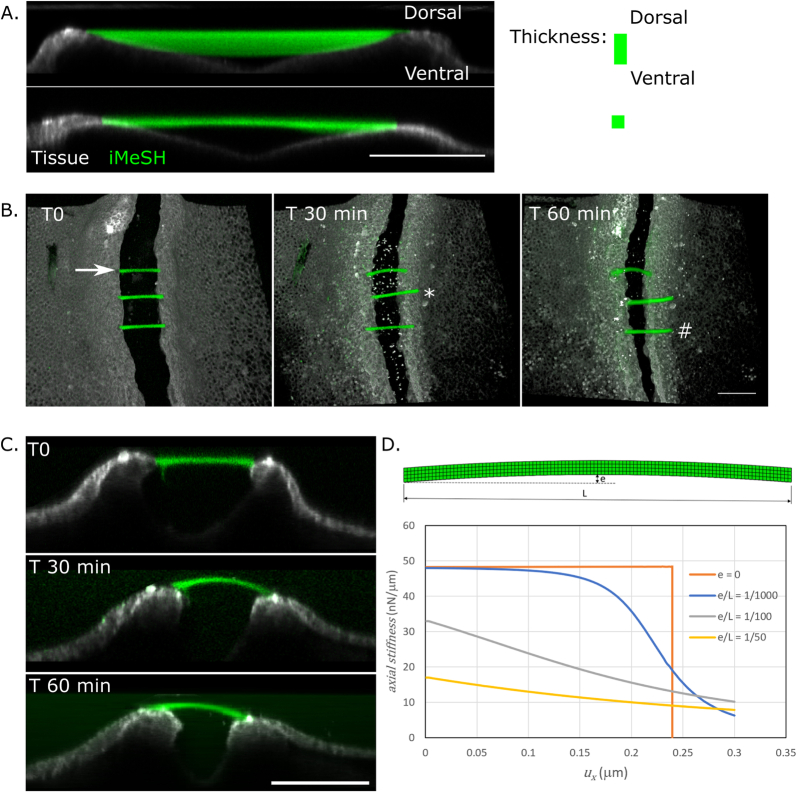
Extended Data Fig. 4. Horizontal bar force sensors.
a. Horizontal bars printed superficially or to greater ventral depth between the neural folds of different embryos, showing ability to generate structures suspended between embryonic tissues.Images are representative of more than 3 replicates of thin and thick structures. b. Time series showing variable deformation of three bars between the neural folds of the same embryo. Arrow: shown in (C). *: quickly detaches. #: initially deforms, then detaches. c. Optical re-slice of the bar indicated by an arrow in (B) showing homogenous dorsal bending. d. Idealised FEM model showing highly non-linear force-displacement relationship between bars with slight differences in initial curvature. Perfectly straight bars (e = 0) resist very high axial force before deforming suddenly. Scale bars = 100 μm throughout.