Fig. 2. Estimates of the fraction of patients attributable to autosomal recessive coding variants in different subsets of genes and patients.
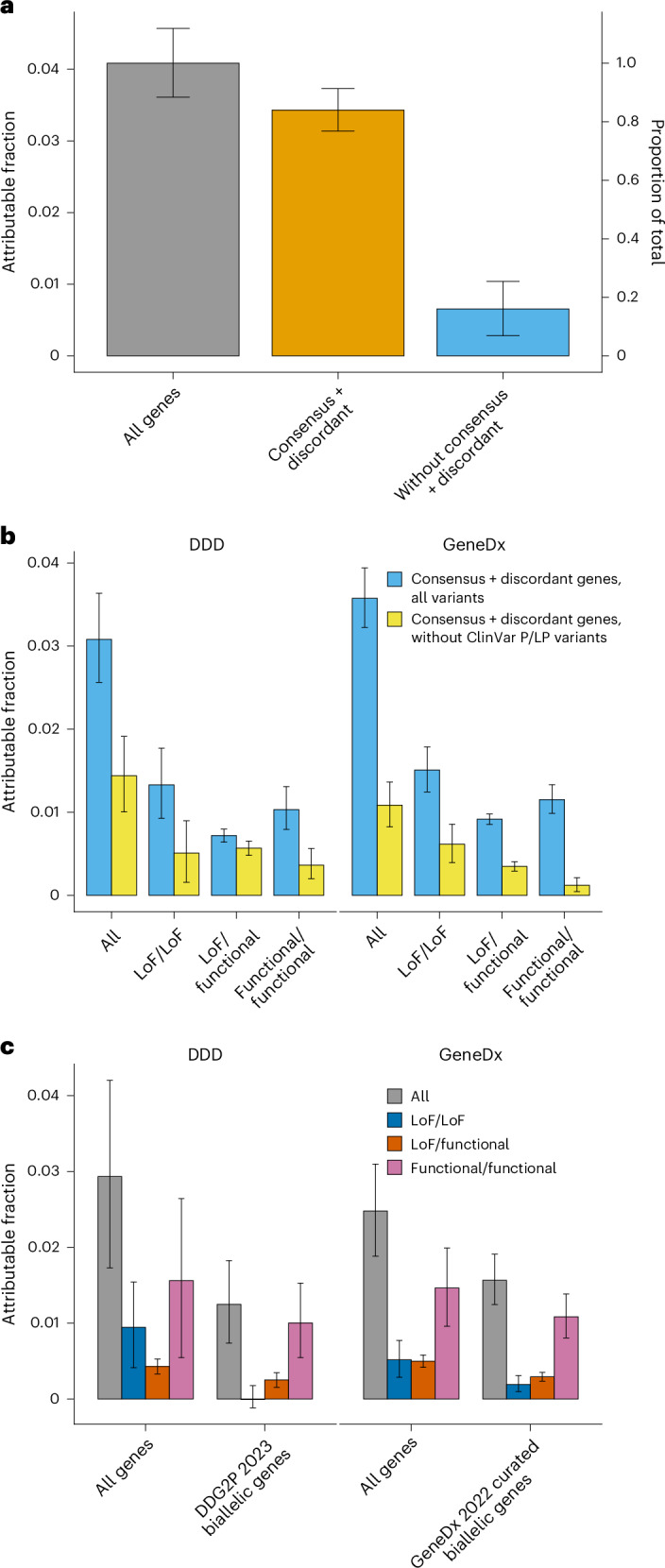
These plots are focused on the individuals without cross-continental admixture from seven large GIA sub-groups, as in Fig. 1 and Table 1. a, Estimates in all individuals from DDD and GeneDx combined (n = 25,523), for all genes versus genes in the indicated lists. b, Estimates in all individuals for consensus + discordant genes split by cohort (n = 7,919 and 17,604 for DDD and GeneDx, respectively), comparing the estimates obtained with all variants versus after removing variants annotated as pathogenic or likely pathogenic (P/LP) in ClinVar. c, Estimates in undiagnosed individuals (n = 4,425 and 12,604 for DDD and GeneDx, respectively), for all genes versus the genes that are used for clinical filtering of diagnostic autosomal recessive variants in the respective cohorts, split by cohort and functional consequence of the variants. Error bars, 95% confidence intervals.
