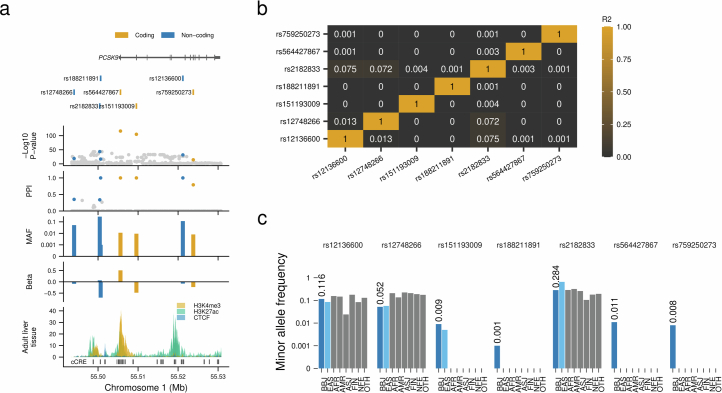
Extended Data Fig. 7. A novel rare non-coding variant in the PCSK9 locus confers very strong association with LDLC levels.
a, Estimated causal variant configuration at the PCSK9 locus for serum LDLC. The horizontal axes indicate genomic coordinates. Beta and P-value were determined by LDLC GWAS (n = 111,048). PPIs were determined by FINEMAP (Methods). The very rare non-coding variant rs188211891 showed a very strong association with the LDLC levels with high PPI. b, Pairwise linkage disequilibrium matrix of 7 putative causal variants in PCSK9 locus for LDLC association. Numeric values inside the rectangles indicate r2. c, Population frequencies of seven putative causal variants in this locus. Population frequencies were obtained from the gnomAD database. Chromatin immune-precipitation data were obtained from ENCODE portal. LDLC, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; MAF, minor allele frequency; PPI, posterior probability of inclusion; AAF, alternate allele frequency; BBJ, Biobank Japan; EAS, East Asian; AFR, African; AMR, Admixed American; ASJ, Ashkenazi Jewish; FIN, Finnish; NFE, non-Finnish European; OTH, others. AAF was obtained from the gnomAD dataset. The numbers of individuals included in the association analysis are found in Supplementary Table 1, and abbreviations for phenotypes are found in Supplementary Table 2.