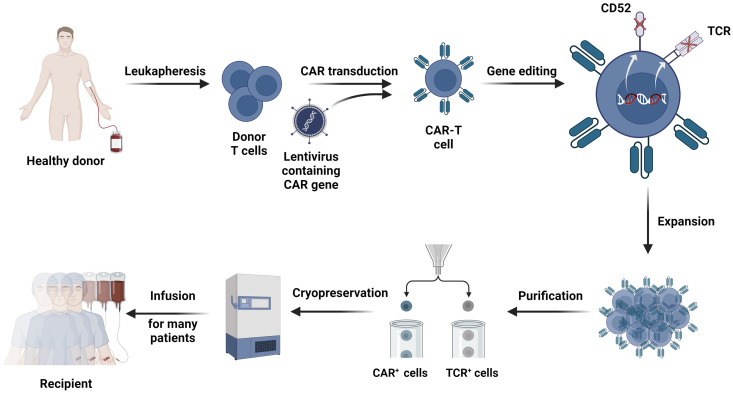
Fig. 1.
The conventional production route of the UCAR-T therapy. The first step in the manufacturing of universal CAR-T cells is the collection of donor T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), which are extracted from the donor through leukapheresis. The T cells are then isolated via magnetic bead technology. The CAR gene is then transduced into the collected T cells by lentivirus. To limit the occurrence of GVHD and HVGR, gene editing techniques are employed to knock down the expression of alloreactive genes (e.g., TCR and CD52). After acquiring stable CAR-T cells, large-scale in vitro expansion is required to obtain the desired dose. The expanded CAR-T cells are further purified to ensure safety. Eventually, the CAR-T cells are cryopreserved and readily available for infusion into multiple patients.