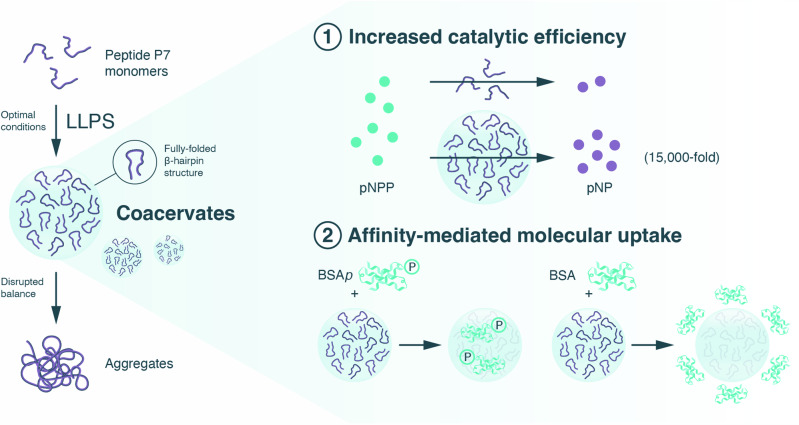
Fig. 1. Illustration of the strategy used in this work, harnessing liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) to enhance peptide catalysis.
Depicted are biomolecular coacervates composed of a single peptide (P7), with densely packed peptide domains (where the fully folded ß-hairpin structure is stabilized), and which are proficient at (1) hydrolyzing phosphate ester molecules (e.g., pNPP, p-nitrophenyl phosphate with a 15,000-fold catalytic efficiency increase over soluble peptides; and 2) selectively sequestering phosphoryl assemblies (e.g., BSAp, phosphorylated Bovine Serum Albumin) through affinity interactions.