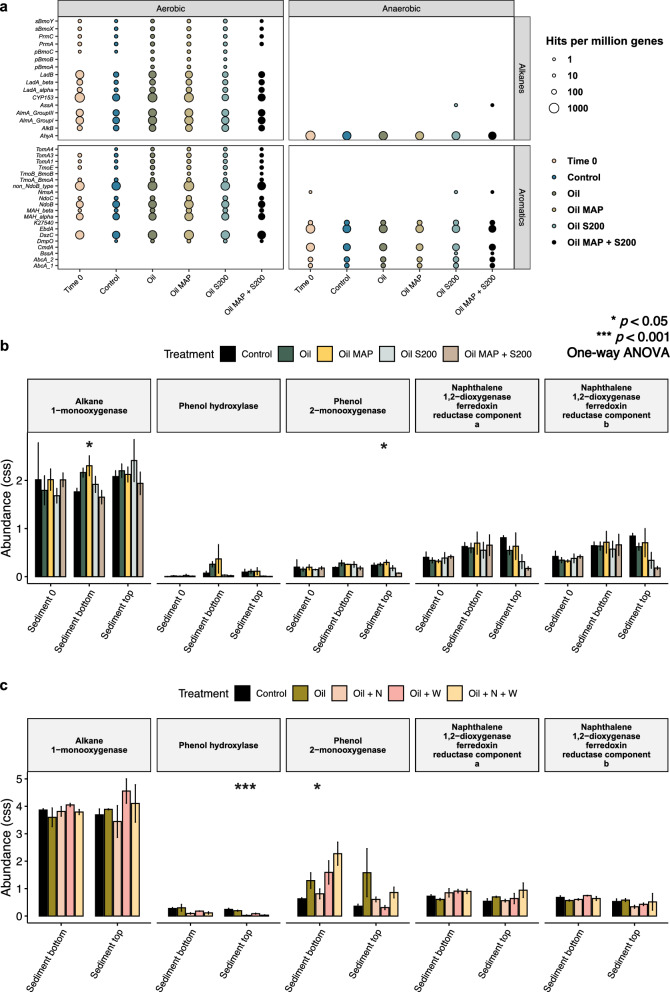
Fig. 4.
Evaluating the hydrocarbon degradation capability of microbial communities from Arctic beach sediments after various treatments. a The metagenomes obtained from sediment samples in CI were analyzed using CANT-HYD to identify significant hydrocarbon degradation genes. The relative abundance of 5 key hydrocarbon degradation genes in CI and CII sediments was predicted using PICRUSt2 based on 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing data (b, c). The treatments are labeled as follows: CI—no oil control (Control), oil only (Oil), oil with inorganic fertilizer, MAP (Oil MAP), oil with oleophilic fertilizer, S200 (Oil S200), and oil with both fertilizers (Oil MAP + S200); CII—no oil control (Control), oil only (Oil), oil with both fertilizers (Oil + N), oil with SWA (Oil + W), and oil with both fertilizers and SWA (Oil + N + W). The labeling 'Sediment 0' denotes time 0, 'Sediment top' corresponds to surface sediment, and 'Sediment bottom' signifies bottom sediment. Additionally, the asterisks “*” and “***” indicate significant differences (p < 0.05, ANOVA and p < 0.001, respectively) among the four different treatments