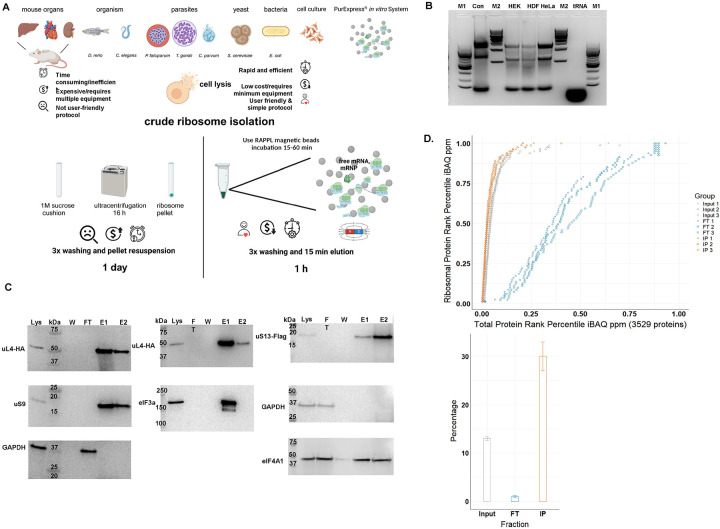
Fig. 1: The RAPPL method.
A. Schematic describing the advantages of RAPPL over conventional methods. B. 2% agarose gel of RAPPLE purified RNA samples from of HEK-293 (HEK), human dermal fibroblasts (HDF) and HeLa human cell cultures. RNA isolated from commercial HeLa cell lysate (Con; Thermo Fisher HeLa IVT kit) and purified yeast tRNAs (tRNA, Ambion) were loaded as controls. NEB 100 bp and 1 Kb base pair markers (M1 and M2, respectively) are used to estimate size of isolated RNAs. C. Western blot analysis of HEK-293 lines uL4-HA and uS13-Flag tagged by CRISPR/Cas9 throughout the RAPPL purification process – lysate (Lys), flow-through (FT), wash (W) and elution (E1 and E2). RAPPL is selective for ribosome-associated factors, showing that the HA-tagged ribosomal protein uL4, Flag-tagged uS13, as well as the untagged uS9 are in the elution fractions. Translation factors are also enriched and purified by RAPPL as seen by the visualization of eIF3A and eIF4A1 proteins by specific antibodies in elution fractions. Presence of GAPDH, as a control for loading is detected in lysate and flow-through. Molecular markers indicate size of detected proteins. D. (top) Plot of the of each HEK-293 ribosomal protein’s rank percentile in relation to total protein rank percentile for each replicate of input, flow-through (FT), and bead-bound (IP) fractions. (bottom) Graph representing percentage of ribosomal proteins in total protein associated with input, flow-through (FT), and poly-lysine bead-bound (IP) fractions. Error bars represent standard deviation of triplicate averages.