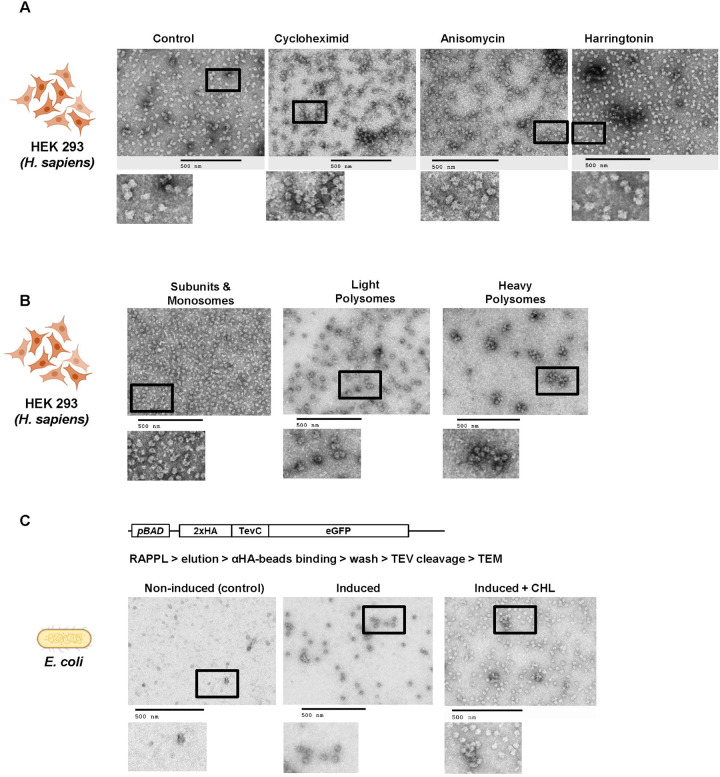
Fig. 4: The elutions of RAPPL can be used in downstream applications.
A. HEK-293 lysates were treated with cycloheximide, anisomycine, and harringtonine with untreated lysate as a control. Ribosomes were purified using RAPPL in the presence of inhibitors and the eluates visualized by TEM. B. HEK-293 lysates were fractionated using polysome profiling. Fractions corresponding to ribosome subunit and monosomes, light polysomes, and heavy polysomes were pooled, respectively. These pools were diluted 1:5 to ensure that sucrose did not interfere with binding. The diluted, pooled samples were subject to RAPPL and the eluates visualized by TEM. C. Schematic of arabinose-inducible reporter expressing a 2xHA affinity tagged eGFP reporter separated by a TEV protease cleavage site (top). RAPPL was performed on bacterial lysates in the absence or presence of bacterial translation elongation inhibitor chloramphenicol (CHL) followed by αHA magnetic bead purification, again ±CHL, finally eluting with TEV protease. Eluates were visualized by TEM. Non-induced are shown as controls for lack of protein production and subsequent non-specific binding to αHA beads. The scale bar represents 500 nm.