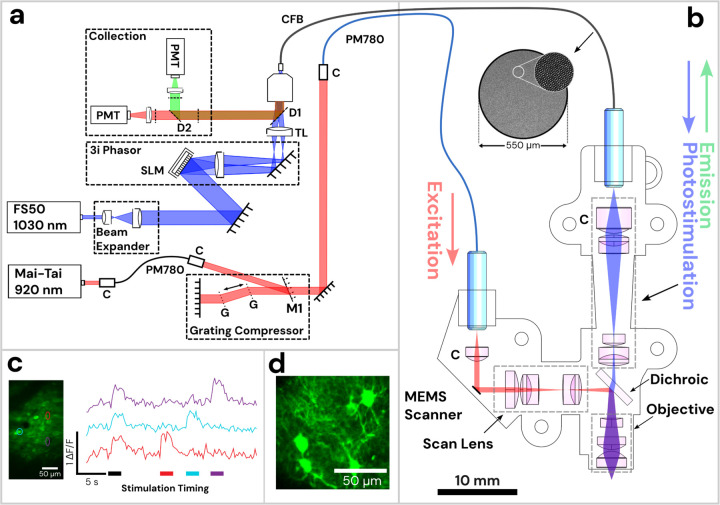
Figure 1: Diagram of Opto2P-FCM miniature two-photon microscope with optogenetic stimulation.
(a) Schematic of the lasers and detection system. The 920 nm pulsed laser is coupled into a polarization maintaining fiber (PM780) for spectral broadening and a transmission grating-pair compressor for dispersion compensation. The output is coupled to a second PM780 fiber to relay to the miniature microscope. A 1030 nm pulsed laser is beam-expanded and reflected off of a spatial light modulator (SLM) for holographic spatial patterning. The spatially patterned beam is focused onto a coherent imaging fiber bundle (CFB) to relay the patterned light to the miniature microscope. Fluorescence is collected back through the same CFB, separated by dichroics and detected on two photomultipliers (PMTs). (b) Schematic of miniature microscope with detailed layout of optical components and beam path. The 920 nm laser output from the PMF is collimated and reflected off of a MEMS scanner and passes through a scan lens consisting of a plano-convex and achromatic lens to generate a telecentric scan across the imaging plane. Patterned photostimulation light at 1030 nm exits the CFB, is collimated using an aspheric lens, combined with the 920 nm light using a dichroic mirror and focused through the same objective. The miniature objective is designed with a working distance of 1.5 mm to focus both 920 nm and 1030 nm light to the same imaging plane. (c) In vivo demonstration of head-attached two-photon imaging and selective optogenetic two-photon photostimulation in a freely moving mouse. Imaging was performed in the visual cortex with neurons co-expressing the calcium indicator jGCaMP7s and the opsin ChRmine. Two-photon photostimulation was performed on three selected regions of interest (ROI) in the imaging field (see outlines on the maximum intensity projection image). An image time sequence was acquired whereby all three ROIs were illuminated simultaneously (indicated by black stimulation timing bar) followed by each individual ROI sequentially (indicated by color matched bars). ΔF/F traces of jGCaMP7s show responses in the ROIs that occur synchronously with photostimulation. (d) The resolution of the Opto2P-FCM provides visualization of processes from somatosensory cortex neurons expressing jGCaMP7s.