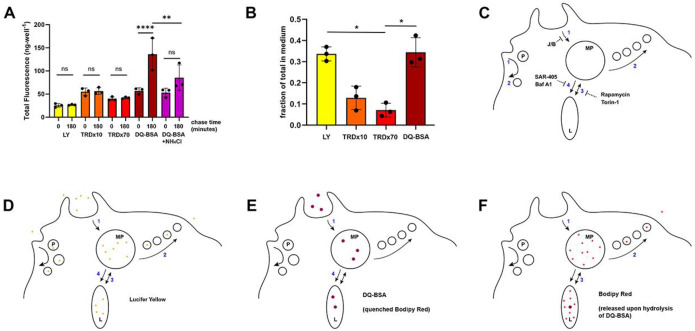
Figure 6. Small molecules generated by protein degradation in lysosomes recycle from the cell.
(A, B) Efflux of LY, TRDx10, TRDx70 and DQ-BSA (Bodipy Red). (A) Macrophages were incubated with the indicated fluorophores for 2 hr in BMM, then were washed and the medium was replaced with Ringers Buffer with BSA and CSF1 for 0 or 180 min. Chase medium was removed and cells were lysed to measure cell-associated fluorescence. Total fluorescence in the chase medium and cell-associated fluorescence were calculated for each well. Total fluorescence of LY, TRDx10 and TRDx70 were constant, confirming that the probes were not altered or degraded in the cells. The fluorescence of DQ-BSA increased significantly due to dequenching of the fluorophore Bodipy Red upon its release from the BSA by lysosomal hydrolysis. That increase was diminished by inclusion of 10 mM NH4Cl in the chase medium. One way ANOVA of the indicated pairs: ns: not significant, **, p<0.01; ****, p<0.0001.
(B) The fraction of internalized probe that recycled to the medium was inversely proportional to the probe size. Recycling efficiency of Bodipy Red (from DQ-BSA) resembled the efficiency of the small probe LY.
(C) Model for pinocytic solute influx and retrograde flow during cell growth. In the absence of CSF1, most pinocytosis is via small pinosomes (P) which recycle fluid and send relatively small quantities of ingested solutes to lysosomes. CSF1 stimulates macropinosome formation (MP) by macropinocytosis (1), which can be inhibited by J/B. Membrane and a small fraction of internalized solutes recycle from macropinosomes in small vesicles (fast recycling, 2). Macropinosomes interact with lysosomes either by pyranhalysisis, with transient small bridging connections between the organelles (3) or by complete merger of macropinosome content and membrane into lysosomes (4). We propose that the former is inhibited by rapamycin and Torin-1 and the latter is inhibited by SAR-405 and Bafilomycin A1.
(D) Lucifer yellow reports movement through all these pathways.
(E) Being larger than LY, DQ-BSA enters primarily in macropinosomes and is restricted by its size-limited traffic itinerary to the more direct fusion with lysosomes.
(F) Upon degradation of DQ-BSA in lysosomes and release of Bodipy TR-X into the lumen, the smaller fluorophore recycles efficiently from the cell, moving retrograde via size-selective interactions with macropinosomes.