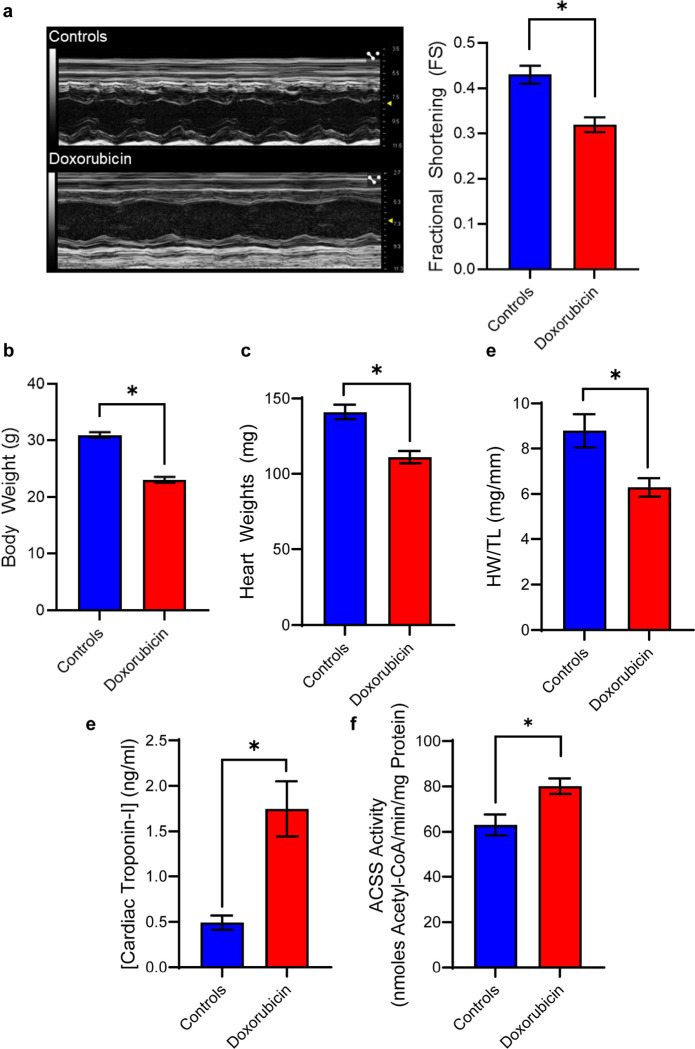
Figure 3.
Indicators of Pathology in Mouse Model of Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity. (a) Doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction was determined by decreased fractional shortening ratios acquired from echocardiograms. (mean ± S.E.M.; n = 4–8, *p < 0.05, independent t-test). (b) Mice (mean ± S.E.M.; n = 14, *p < .05, independent t-test) and (c) hearts (mean ± S.E.M.; n = 14, *p < .05, independent t-test) were weighed post-mortem. (d) Tibia lengths were also measured to generate heart weight to tibia length ratios (HW/TL) (mean ± S.E.M.; n = 3–6, *p < .05, independent t-test). (e) Serum cardiac troponin-I concentrations were determined by ELISA (mean ± S.E.M.; n = 8–10, *p < .05, independent t-test) (f) Acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family (ACSS) activity was determined by evolution of pyrophosphate by product in heart homogenates (mean ± S.E.M.; n = 9, *p < .05, independent t-test).