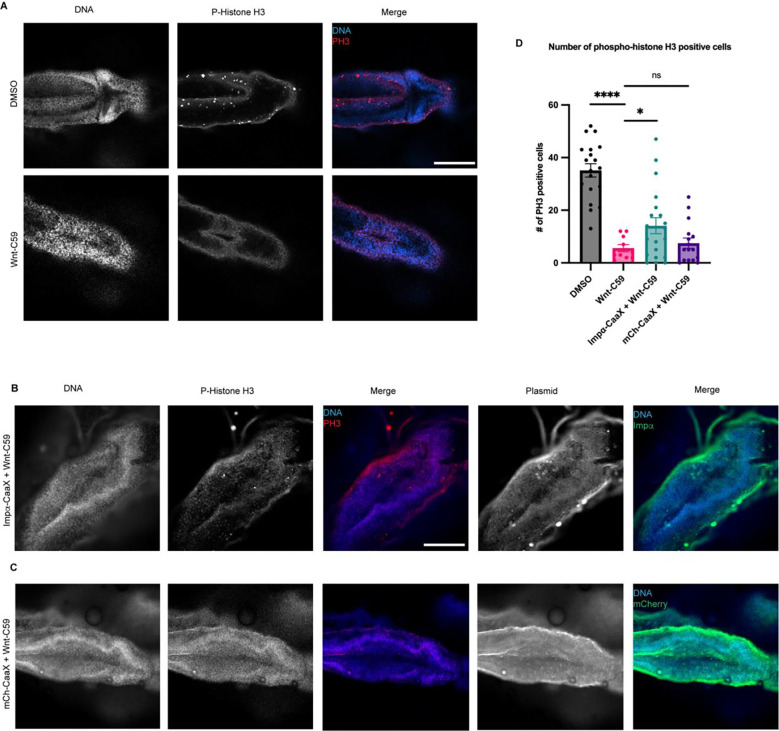
Figure 5. Overexpression of CaaX Modified Importin α in the Developing X. laevis Brain Partially Rescues Developmental Defects due to PORCN Inhibition.
A) Confocal images of NF stage 42 X. laevis brains from X. laevis grown in the presence of DMSO or 100μM Wnt-C59 immunostained for phospho-histone H3, a marker of actively dividing cells. Scale bar = 250μm.
B) Confocal images of NF stage 42 X. laevis brains from X. laevis expressing importin α modified with a c-terminal CaaX domain which forces cortical localization via farnesylation and grown in the presence of 100μM Wnt-C59 immunostained for phospho-histone H3 and the modified importin α-CaaX construct.
C) Confocal images of NF stage 42 X. laevis brains from X. laevis expressing an mCherry construct modified with a c-terminal CaaX domain and grown in the presence of 100μM Wnt-C59 immunostained for phospho-histone H3 and the modified CaaX construct.
D) Quantification of the number of phospho-histone H3 positive cells in stage 42 X. laevis brains of X. laevis grown in the presence of DMSO or 100μM Wnt-C59 and expressing importin α-CaaX or mCherry-CaaX. Wnt-C59 treated X. laevis embryos showed a significantly reduced number of phospho-histone H3 positive cells in the brain compared to DMSO treated X. laevis. X. laevis embryos expressing importin α-CaaX in the brain display a partial rescue of the reduced phospho-histone H3 levels which was not recapitulated in X. laevis expressing mCherry-CaaX. Mean +/− SEM n>10 *=p<0.05 ****=p<0.0001 determined by Student’s t-test.