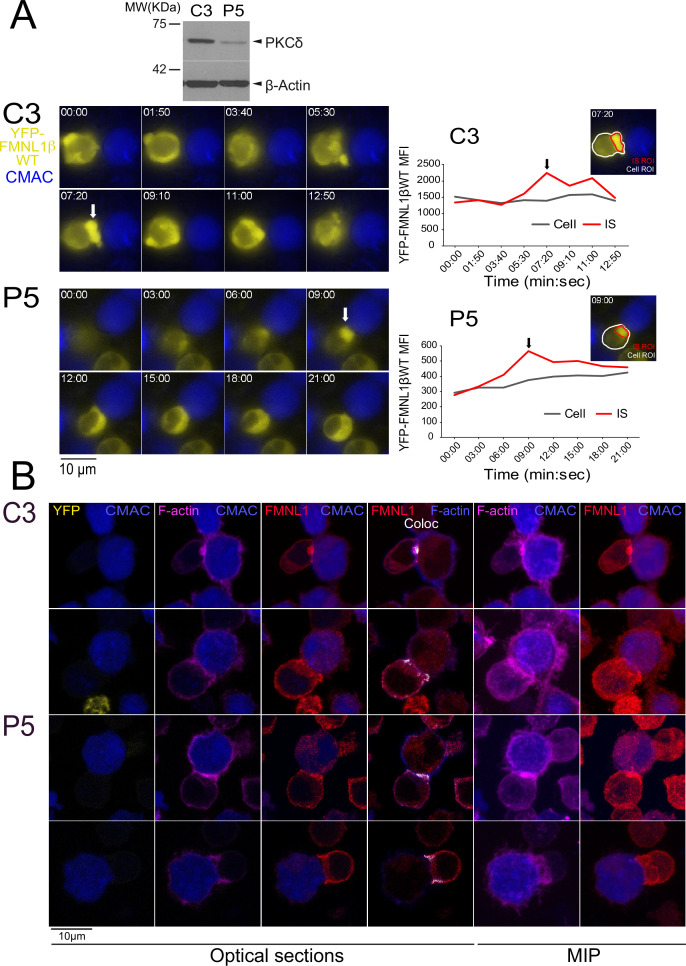
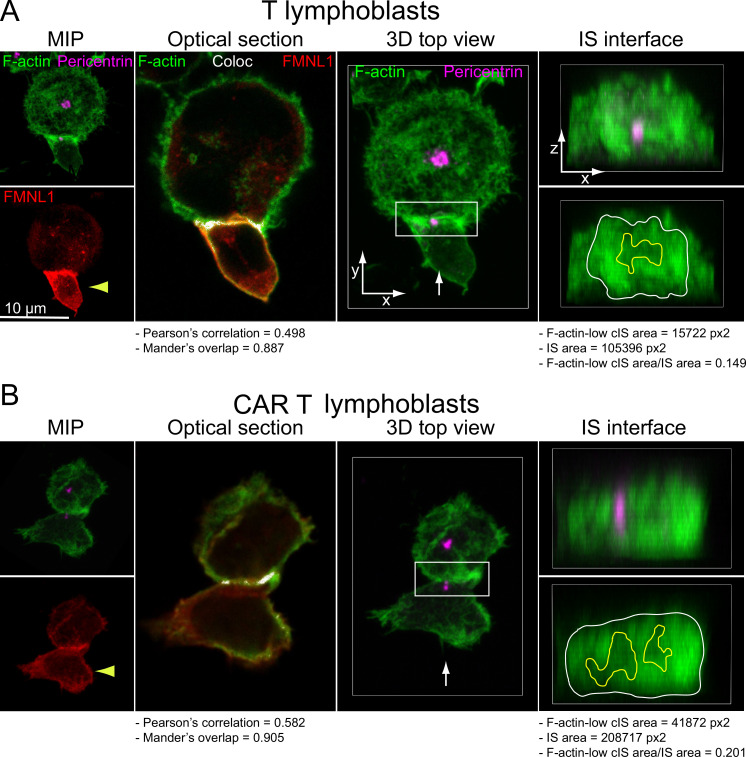
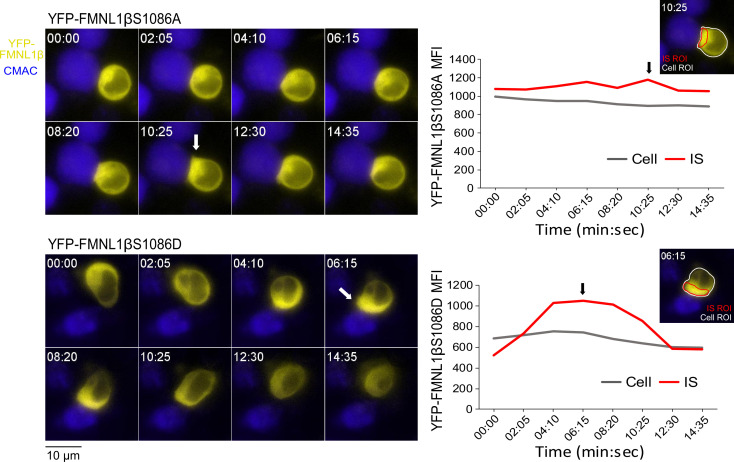
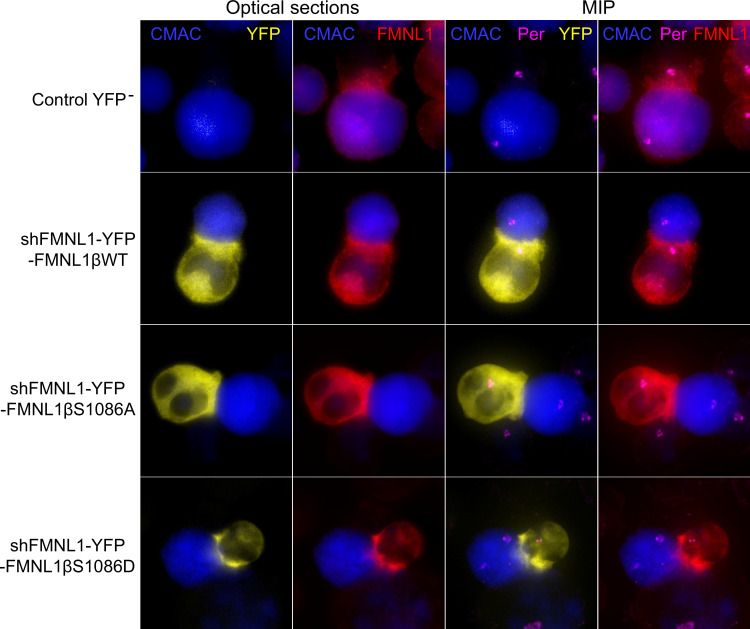
Figure 6. FMNL1β recruitment to the immune synapse (IS) is protein kinase C δ (PKCδ)-independent.
C3 control and P5 PKCδ-interfered cells were transfected with FMNL1-interfering expressing interference-resistant YFP-FMNL1βWT (shFMNL1-HA-YFP-FMNL1βWT) plasmid. Subsequently, both transfected clones were simultaneously challenged with CMAC-labeled, SEE-pulsed Raji cells (blue) attached to slides and time-lapse acquisition of emerging synapses was performed as indicated in Materials and methods. The videos (7 fps) (Figure 6—video 1) were captured and in (A), left, representative frames from videos of each clone are shown. White arrows indicate accumulations of YFP-FMNL1βWT at the IS. Western blot (WB) analysis of cell lysates from both clones (top inset) shows PKCδ silencing in P5 clone. In the right side, YFP-FMNL1βWT mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) within the cell regions of interest (ROI) (gray line) and the IS ROI (red line) are represented. The inserts in the graphs include the cell ROI (white) and the IS ROI (red) used for the time-lapse measurements on representative frames for both clones. Results are representative of the data from several videos (n=6 for each clone) with similar results. (B) Control C3 (upper rows) and P5 PKCδ-interfered cells (lower rows) were simultaneously challenged with CMAC-labeled SEE-pulsed Raji cells (blue) attached to slides. After 1 hr, synapses were fixed and immunofluorescence developed with anti-FMNL1 (red) to label endogenous FMNL1 and phalloidin (magenta) to label F-actin. Synapses were imaged with confocal fluorescence microscopy and colocalization pixels between FMNL1 (red) and F-actin (acquired in magenta, changed to blue in the fourth column) are represented in white. Representative optical sections of synapses formed by both clones are shown in the left columns. The colocation coefficients were: first row, Pearson = 0.50, Manders-=0.877; second row, Pearson = 0.431, Manders = 0.864; third row: Pearson = 0.434, Manders = 0.838; fourth row, Pearson = 0. 484, Manders = 0.794. Maximum intensity projection (MIP) images of the same synapses are shown in the two far-right columns. Results and ANOVA are representative of data from several independent experiments (n=3) with similar results.