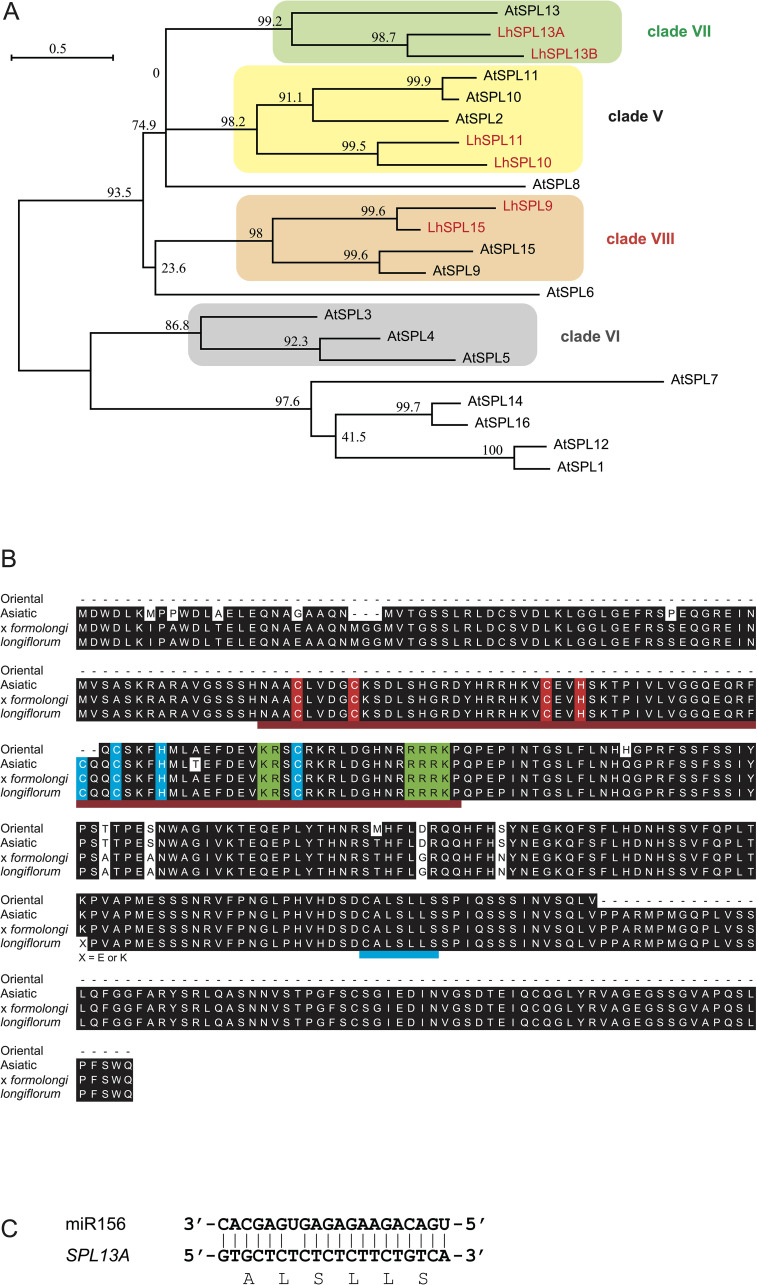
Figure 1.
(A) A phylogenetic tree of SPL proteins in lilies (red letters) and Arabidopsis. Numbers next to nodes indicate bootstrap value (%). Bar indicates genetic distance 0.5. The accession numbers of Arabidopsis sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S2 . (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of SPL13A in Oriental hybrid lily ‘Dizzy’ (Oriental), Asiatic hybrid lily ‘Lollypop’ (Asiatic), Lilium × formolongi ‘Raizan 2’ (× formolongi), and L. longiflorum ‘White Heaven’ (longiflorum). The Oriental sequence was partial, and the L longiflorum sequences had two heterozygous sequences, in which one amino acid differed. Dark red underlines indicate the SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein domain (Yamasaki et al., 2004) and a blue underline exhibits the miR156 binding region. The two conserved zinc finger structures (Zn-1, red background, and Zn-2, blue background) and NLS (green background) are shown. (C) Base pairs between miRNA156 and SPL13A.