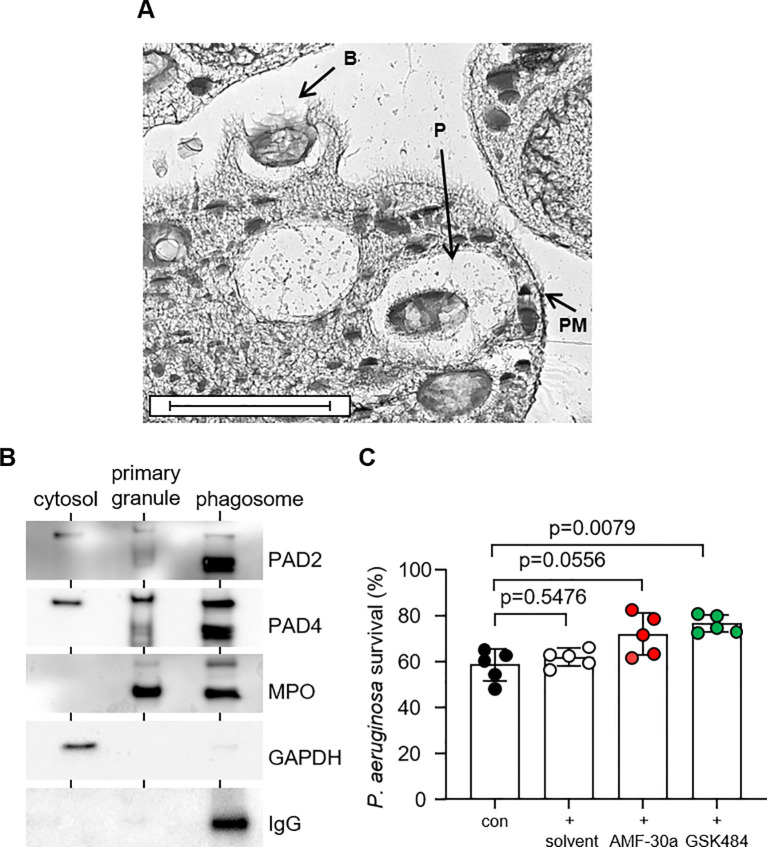
Figure 3.
PAD2 and PAD4 are degranulated into the bacterial phagosome and participate in bacterial killing. (A) Representative micrograph showing neutrophil forming pseudopodia at the time of engulfment and bacteria inside phagocytic vacuoles following 3 min of incubation [Labels indicate bacteria (B), phagosomes (P), and plasma membrane (PM); scale bar, 2 μm]. (B) Western blot analysis of neutrophil cytosol, primary granules and phagosome fractions for PADs, including primary granule and phagosome marker MPO, and cytosolic marker GAPDH. Representative images of n = 3 biological replicates. (C) P. aeruginosa survival following 30 min of neutrophil (5 × 107/mL) phagosomal killing (MOI = 4; 1 neutrophil to 4 bacteria) (con). Neutrophils were pre-treated with PAD inhibitors AMF-30a (50 µM) or GSK484 (50 µM) for 15 min prior to killing assays. DMSO [0.5% (v/v)] was used as the solvent control. Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparison Tukey’s post-hoc test and presented as mean ± SEM, n = 5 biological replicates.