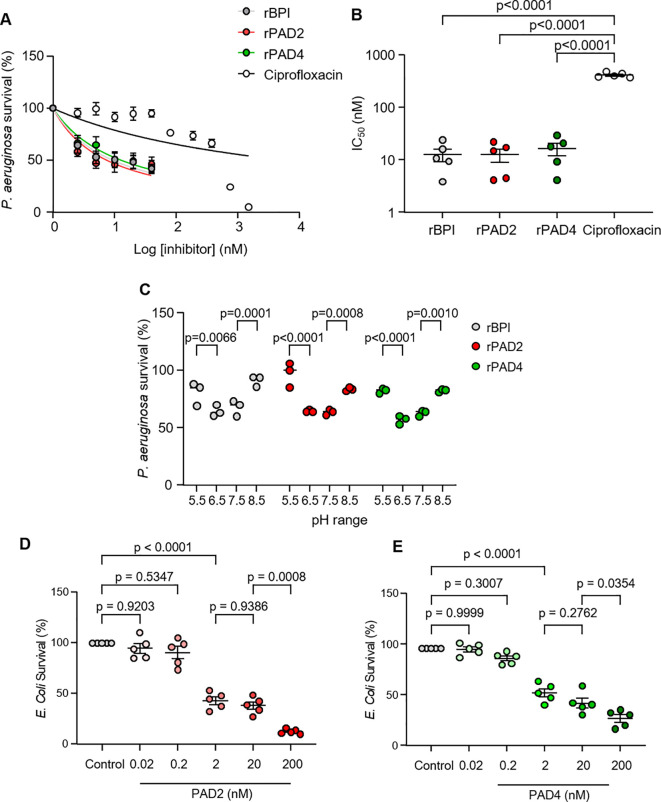
Figure 5.
Recombinant human PAD2 and PAD demonstrate dose-dependent killing of P. aeruginosa and E coli. (A) Survival of P. aeruginosa (5 × 105 CFU/mL) 30 min after incubation with rPAD2, rPAD4, rBPI (2.5–40 nM), or ciprofloxacin (2.5–1500 nM) in PBS (pH 7.4). Survival (%) calculated relative to untreated P. aeruginosa. Data expressed as a non-linear regression and presented as mean ± SEM, n = 5 biological replicates repeats. (B) Compounds were tested for activity against P. aeruginosa and MIC50 values calculated. (C) Survival of P. aeruginosa (5 × 105 CFU/mL) 30 min after incubation with rPAD2, rPAD4, or rBPI (20 nM) in PBS (pH 5.5, 6.5, 7.5, or 8.5). Survival (%) calculated relative to P. aeruginosa CFU/mL in 0 nM enzyme at respective pH levels. (D, E) Survival of E Coli (5 × 105 CFU/mL) 60 min after incubation with rPAD2 (D) or rPAD4 (E) in PBS (pH 7.4) (n = 5 biological replicates). Data were analyzed by one-way or two-way ANOVA, followed by multiple comparison Tukey’s post-hoc test and presented as mean ± SEM.