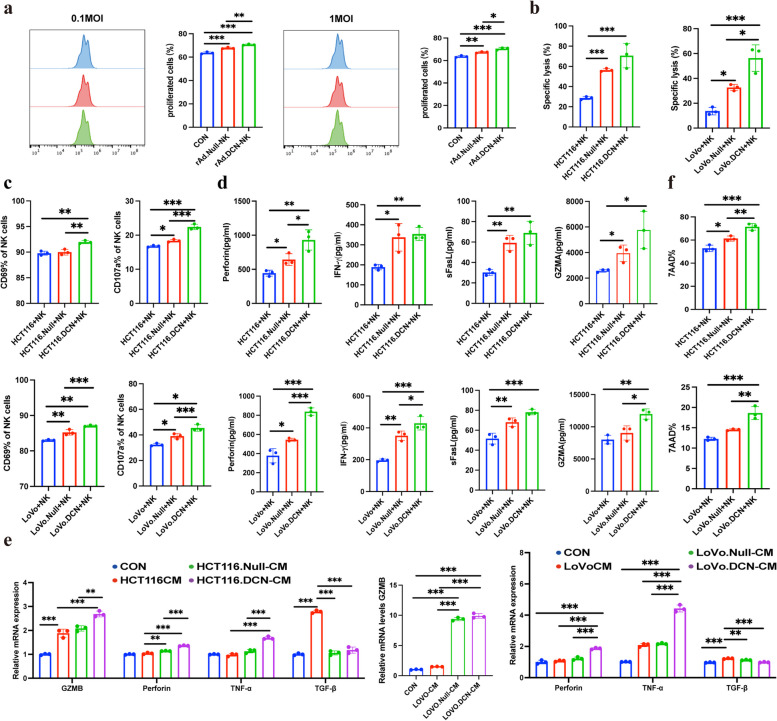
Fig. 2.
rAd.DCN enhances cytotoxic activity of NK cells in vitro. a NK cells were pre-stained with CFSE (5 µM) and then infected with Oncolytic Viruses (OVs) at MOIs of 0.1 and 1 for 72 h. Flow cytometry was utilized to analyze the proliferation of NK cells. b NK cells were co-incubated with rAd.Null or rAd.DCN (50 MOI) pretreated HCT116 cells or LoVo cells for 4 h, and a cytotoxicity assay was performed. The percentage of specific cell lysis of HCT116 and LoVo cells was analyzed. c NK cells were co-cultured with rAd.Null or rAd.DCN (50 MOI) pretreated HCT116 or LoVo cells for 4 h, and flow cytometry was used to detect the percentage of CD69 and CD107 positive NK cells. d Co-incubated supernatants were collected and assayed for perforin, IFN, sFasL, and GZMA secretion using the LEGENDplex™ Human CD8/NK Panel Kit. e NK cells were treated with the supernatant of control or OVs-infected HCT116 or LoVo cells for 48 h, and the expression of granzyme B, perforin, TNF-α, and TGF-β of NK cells was evaluated by qPCR assay. f HCT116 or LoVo cells pretreated with rAd.Null or rAd.DCN (50 MOI) were labelled using CFSE, and after co-culturing with NK cells for 4 h, the cells were collected and labelled with 7AAD, and apoptosis rate of target cells was detected by flow cytometry. One-way ANOVA was used for comparisons between multiple groups. All results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns means no significance