Abstract
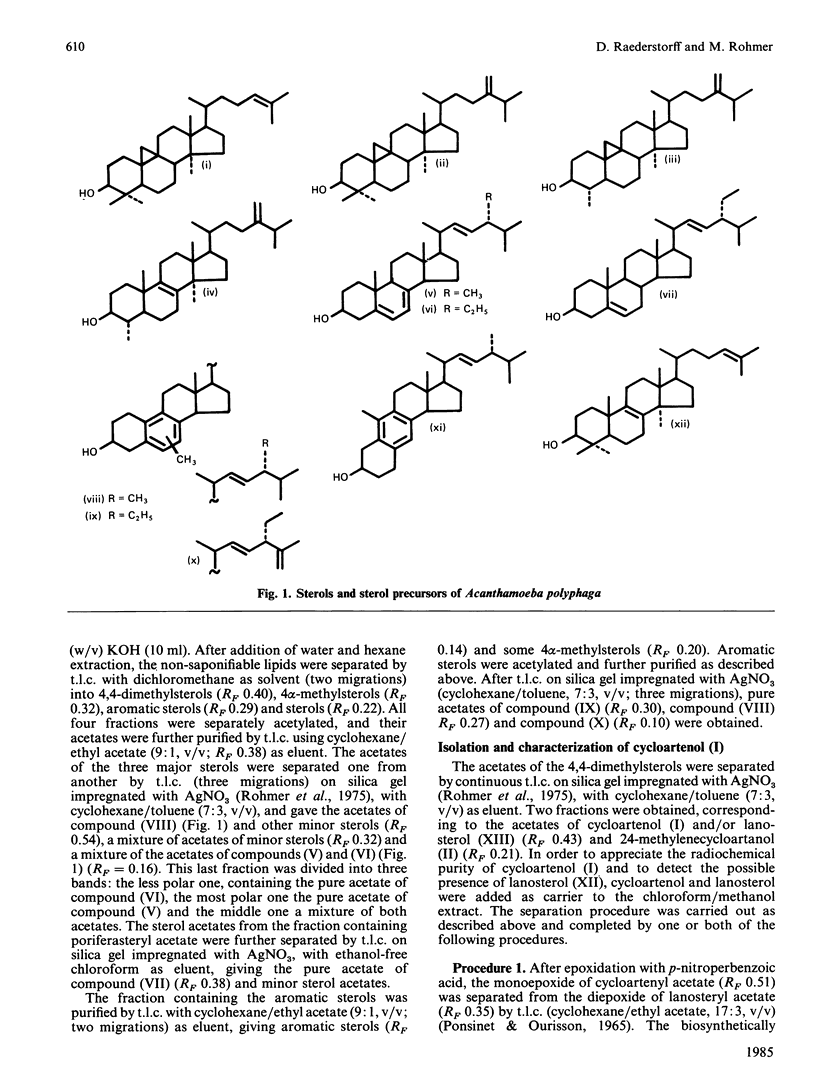
The soil amoeba Acanthamoeba polyphaga is capable of synthesizing its sterols de novo from acetate. The major sterols are ergosterol and poriferasta-5,7,22-trienol. Furthermore C28 and C29 sterols of still unknown structure with an aromatic B-ring are also synthesized by the amoeba. The first cyclic sterol precursor is cycloartenol, which is the sterol precursor in all photosynthetic phyla. No trace of lanosterol, which is the sterol precursor in animals and fungi, could be detected. These results show that at least some of the biochemical processes of Acanthamoeba polyphaga might be phylogenetically related to those of unicellular algae. Addition of exogenous sterols to the culture medium does not influence the sterol biosynthesis and the sterol composition of the cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste P., Hewlins M. J., Fritig B. La biosynthèse des stérols dans les tissus de tabac cultivés in vitro. Cinétique de formation des stérols et de leurs précurseurs. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jul;9(4):526–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Hallmann D., Poralla K., Eibl H. Interaction of hopanoids with phosphatidylcholines containing oleic and omega-cyclohexyldodecanoic acid in lipid bilayer membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1983 Dec;34(1):7–24. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(83)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseret P., Wolff G., Albrecht A. M., Tanaka T., Nakatani Y., Ourisson G. A direct study of the cohesion of lecithin bilayers: the effect of hopanoids and alpha, omega-dihydroxycarotenoids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger L. M., Rees H. H., Ghisalberti E. L., Goad L. J., Goodwin T. W. Biosynthesis of 24-ethylcholesta-5,22,25-trien-3-beta-ol, a new sterol from Clerodendrum campbellii. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):197–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1180197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosworth N., Emke A., Midgley J. M., Moore C. J., Whalley W. B., Ferguson G., Marsh W. C. Unsaturated steroids. Part 2. A novel route to anthrasteroids: X-ray crystal structure of 1(10 leads to 6)abeo-cholesta-5,7,9-trien-3-yl p-bromobenzoate. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1977;(8):805–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner R. L., Landrey J. R., Burns C. H., Mallory F. B. Cholesterol inhibition of pentacyclic triterpenoid biosynthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1968 Aug;15(3):600–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner R. L., Landrey J. R., Kaneshiro E. S., Van Wagtendonk W. J. The metabolism of stigmasterol and cholesterol by Paramecium aurelia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 13;239(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson C. G. The pathogenicity of soil amebas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:231–254. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr-Harf C., Molet B., Schreiber J., Kremer M. Epidémiologie des amibes libres dans les eaux de Strasbourg. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1978 Sep-Oct;53(5):467–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson K. A., Davis F. M., Conner R. L., Landrey J. R., Mallory F. B. Effect of sterol replacement in vivo on the fatty acid composition of Tetrahymena. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6998–7005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. F., Goad L. J., Goodwin T. W., Nes W. R. Concerning the role of lanosterol and cycloartenol in steroid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3967–3976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad L. J. Sterol biosynthesis. Biochem Soc Symp. 1970;29:45–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy S., Avivi L., Katan H. Sterols of soil amoebas and Ochromonas danica: phylogenetic approach. J Protozool. 1966 Aug;13(3):480–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1966.tb01945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy S., Finkelstein S. Lipid composition of soil amoebae. J Protozool. 1965 May;12(2):250–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1965.tb01846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz R., Benveniste P., Bimpson T. Evidence for the presence of an enzyme capable of opening the cyclopropane ring of cycloeucalenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):766–772. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz R., Benveniste P. Plant sterol metabolism. Enzymatic cleavage of the 9beta, 19beta-cyclopropane ring of cyclopropyl sterols in bramble tissue cultures. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4267–4274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannenberg E., Poralla K. The influence of hopanoids on growth of Mycoplasma mycoides. Arch Microbiol. 1982 Dec;133(2):100–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00413519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D., Ulsamer A. G., Weihing R. R., Wetzel M. G., Wright P. L. The enzymatic aromatization of the B ring of delta5,7-sterols. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 17;187(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowit J. D., Fulton C. Purification and properties of flagellar outer doublet tubulin from Naegleria gruberi and a radioimmune assay for tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3638–3646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazaki T., Hori H., Osawa S. Phylogeny of protozoa deduced from 5S rRNA sequences. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(6):411–419. doi: 10.1007/BF02102316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine N. D., Corliss J. O., Cox F. E., Deroux G., Grain J., Honigberg B. M., Leedale G. F., Loeblich A. R., 3rd, Lom J., Lynn D. A newly revised classification of the protozoa. J Protozool. 1980 Feb;27(1):37–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallory F. B., Conner R. L. Dehydrogenation and dealkylation of various sterols by Tetrahymena pyriformis. Lipids. 1971 Mar;6(3):149–153. doi: 10.1007/BF02533028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nes W. R., Alcaide A. Dealkylation of 24-ethylsterols by Tetrahymena pyriformis. Lipids. 1975 Mar;10(3):140–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02534151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neunlist S., Holst O., Rohmer M. Prokaryotic triterpenoids. The hopanoids of the purple non-sulphur bacterium Rhodomicrobium vannielii: an aminotriol and its aminoacyl derivatives, N-tryptophanyl and N-ornithinyl aminotriol. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poralla K., Kannenberg E., Blume A. A glycolipid containing hopane isolated from the acidophilic, thermophilic Bacillus acidocaldarius, has a cholesterol-like function in membranes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohmer M., Bouvier P., Ourisson G. Molecular evolution of biomembranes: structural equivalents and phylogenetic precursors of sterols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):847–851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohmer M., Brandt R. D. Les stèrols et leurs prècurseurs chez Astasia longa Pringsheim. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):446–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Korn E. D. 7-Dehydrostigmasterol and ergosterol: the major sterols of an amoeba. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):405–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., O'Dell W. D. The influence of growth medium on axenic cultivation of virulent and avirulent Acanthamoeba. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jun;143(2):474–478. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Bambery R. J., Nozawa Y. Further studies of the lipid composition and biochemical properties of Tetrahymena pyriformis membrane systems. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4441–4447. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulsamer A. G., Smith F. R., Korn E. D. Lipids of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Composition and effects of phagocytosis on incorporation of radioactive precursors. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):105–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman R. A., Korn E. D. Uptake of fatty acids by Acanthamoeba. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 4;116(2):229–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowski Z. A., Goad L. J., Goodwin T. W. S-adenosyl-L-methionine-cycloartenol methyltransferase activity in cell-free systems from Trebouxia sp. and Scenedesmus obliquus. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):405–412. doi: 10.1042/bj1360405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


