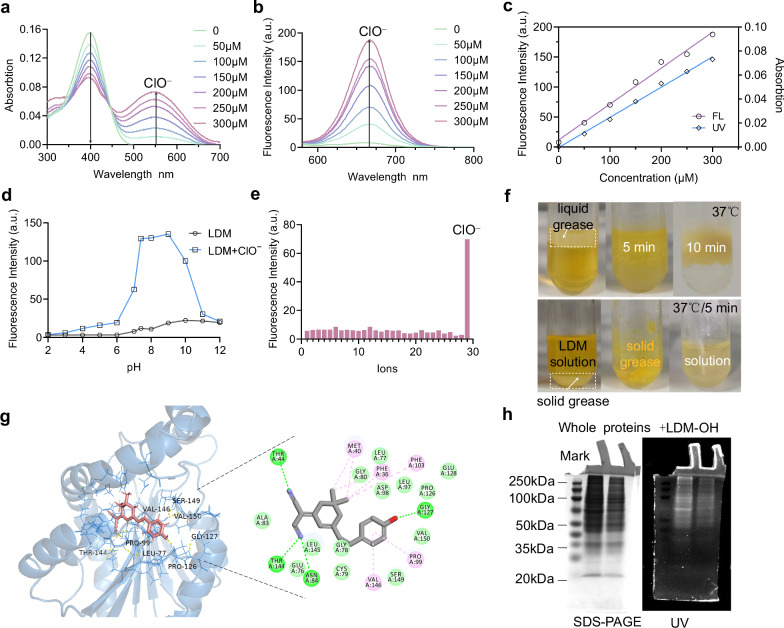
Fig. 2. Optical selectively, physical properties characterization of LDM in vitro.
a, b The absorption and fluorescence spectra of LDM (10.0 μM) in different NaClO (0-300.0 μM) solution (DMSO-PBS, 1:99, v/v, pH = 7.4), λex = 561 nm, slit: 5 nm/5 nm/700 V. c Linear relationship between UV absorption and fluorescence intensity and HClO/ClO− concentration in a and b, the linear regression equation is determined as Y = 59658.07143X + 11.58132, with a linear correlation R2 = 0.98933, where X represents the concentration of ClO− and Y represents the fluorescence intensity of LDM at 665 nm (d) The fluorescence intensity change of LDM (10.0 μM) in different pH (2-12) solutions with (red) or without (black) ClO− (100 μM) (λex = 561 nm), e The selectivity of LDM towards ClO−, and various reactive oxygen species in DMSO-PBS solution (100.0 μM, 1:99, v/v, pH = 7.40). 1. Blank; 2.NO2−; 3.t-Buoo−; 4.PO43-; 5.•OH; 6.HPO42-; 7.CH3COO−; 8.F−; 9.Cl−; 10.Ag+; 11.Al3+; 12.Ca2+; 13.Cr3+; 14.Co2+; 15.Fe2+; 16.Fe3+; 17.Mn2+; 18.Ni2+; 19.Pb2+; 20.Zn2+; 21.Cu2+; 22.Hg2+; 23.Cd2+; 24.H2O2; 25.NO; 26.SO42−; 27.ONOO−; 28.1O2; 29.ClO−. f Lipophilic assay for testing the distribution of the LDM in phosphate buffer. LDM molecules dissolved in the lipids, causing the phosphate buffer to change from yellow to colorless, while the lipids transformed from white to yellow, suggest. LDM with a lipid response behavior. g Macromolecular docking of LDM-OH and representative lipoprotein (Q6UX53). h The whole protein SDS-PAGE electrophoresis (left) and UV image for the protein gel incubation with LDM-OH (37 °C, 2 h) (right), indicating the LDM-OH could bind to the whole proteins in HepG2 cells. Three independent biological replicates were performed, and the results were similar. Source data are provided as a source data file.