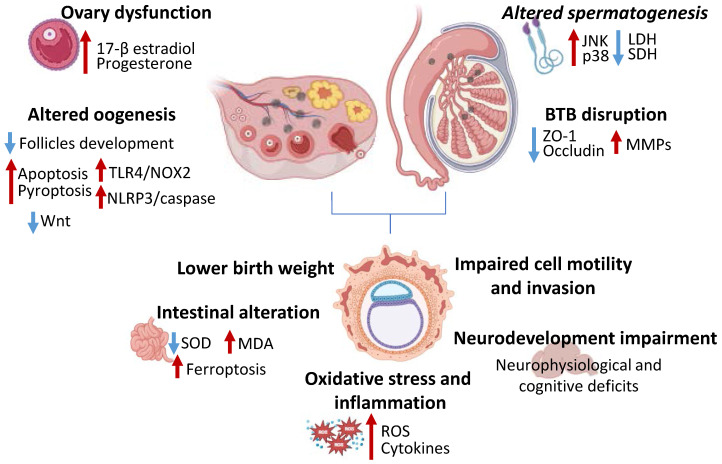
Figure 2.
Effects of MNPs on reproduction. Image showing how MNPs impair ovary-related sexual hormones secretion, reduce follicles development, increase TLR4/NOX2 and NLRP3/caspase pathways, thus triggering apoptosis and pyroptosis and reduce Wnt signaling. MNPs alter spermatogenesis via JNK and p38, and decreasing LDH and SDH activity, moreover, disrupt blood-testis barrier, reducing ZO-1 and occluding expression and increasing MMPs. MNPs affect embryonal development being associated to lower birth weight, impaired cell motility and invasion, altering neural and intestinal development and increasing oxidative stress and inflammation. TLR4—Toll-like receptor 4; NOX2—NADPH Oxidase 2; NLRP3— NOD-like receptor protein 3; JNK—c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; LDH—Lactate dehydrogenase; SDH—Succinate dehydrogenase; ZO-1—zonula occludens 1; MMPs—matrix metalloproteinases; SOD—Superoxide dismutase; MDA—Malondialdehyde; ROS—reactive oxygen species.