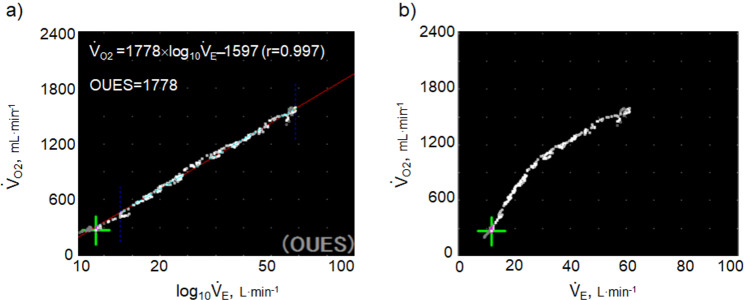
Fig. 1.
Calculation of OUES. a) The relationship between oxygen uptake ( O2: mL ⋅ min−1) and the common logarithm of minute ventilation (
O2: mL ⋅ min−1) and the common logarithm of minute ventilation ( E: L ⋅ min−1) (b) the relationship between
E: L ⋅ min−1) (b) the relationship between  O2 (mL ⋅ min−1) and
O2 (mL ⋅ min−1) and 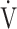 E (L ⋅ min−1).
E (L ⋅ min−1). 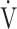 O2 and
O2 and 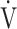 E obtained from breath-by-breath gas-exchange measurements in one COPD patient with GOLD I (75 years old, 64.2 kg) were used. OUES was calculated as the slope of the regression line relating
E obtained from breath-by-breath gas-exchange measurements in one COPD patient with GOLD I (75 years old, 64.2 kg) were used. OUES was calculated as the slope of the regression line relating 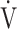 O2 (mL ⋅ min− 1) to the common logarithm of
O2 (mL ⋅ min− 1) to the common logarithm of 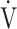 E (L ⋅ min− 1) by the equation:
E (L ⋅ min− 1) by the equation: 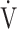 O2 = slope × log 10
O2 = slope × log 10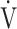 E + intercept. where the constant ‘slope’ is the OUES. Basically, to avoid possible irregular breathing patterns, data from the 3-min resting period, from the first minute of exercise, and from a plateau in
E + intercept. where the constant ‘slope’ is the OUES. Basically, to avoid possible irregular breathing patterns, data from the 3-min resting period, from the first minute of exercise, and from a plateau in 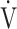 O2 were excluded from the calculation of the OUES. Green cross: exercise starting point; blue crosses: period during which OUES was calculated
O2 were excluded from the calculation of the OUES. Green cross: exercise starting point; blue crosses: period during which OUES was calculated