Table 2.
Incremental exercise variables in COPD patients classified according to the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) criteria
| GOLD spirometric severity | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| I + II (n = 51) | III + IV (n = 71) | p-value | |
| At peak exercise | |||
| Dyspnea, Borg scale | 5.6 (1.8) [5.0 (4.0; 7.0)] | 6.0 (1.9) [6.0 (5.0; 8.0)] | 0.2126 |
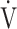 O2, mL⋅min−1 ⋅ kg−1 O2, mL⋅min−1 ⋅ kg−1
|
14.9 (3.8) [15.2 (11.7; 17.3)] | 10.6 (2.3) | < 0.0001 |
| R | 1.10 (0.10) | 1.01 (0.08) [1.01 (0.96; 1.05)] | < 0.0001 |
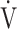 E, L ⋅ min−1 E, L ⋅ min−1
|
43.7 (12.6) | 28.0 (6.6) | < 0.0001 |
| VT, mL | 1397 (320) | 987 (239) | < 0.0001 |
| fR, breaths ⋅ min− 1 | 31.7 (6.1) | 28.9 (5.3) | 0.0079 |
| TI/Ttot | 0.41 (0.05) [0.41 (0.38; 0.43)] | 0.34 (0.05) | < 0.0001 |
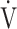 E/ E/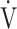 O2 O2
|
49.7 (10.1) | 48.0 (7.4) [47.0 (44.0; 51.2)] | 0.2892 |
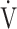 E/ E/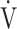 CO2 CO2
|
45.1 (8.7) | 47.8 (8.4) [46.8 (42.7; 51.0)] | 0.1623 |
1−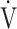 E/MVV, % E/MVV, % |
29.2 (15.4) | 8.4 (19.0) [11.9 (2.9; 19.4)] | < 0.0001 |
| HR, beats ⋅ min− 1 | 124 (17.6) | 112 (16.8) | 0.0005 |
| HR/predicted maximum HR, % | 80.8 (12.4) | 80.0 (10.7) | 0.7007 |
| SpO2, % | 93 (4) [95 (91; 97)] | 91 (5) [92 (87; 94)] | 0.0004 |
| O2 pulse, mL ⋅ beats− 1 | 7.3 (1.9) | 5.4 (1.6) [5.1 (4.2; 6.4)] | < 0.0001 |
| OUES | 1319 (420) | 1135 (440) [1115 (880; 1328)] | 0.0161 |
| ΔFO2, % | 2.58 (0.50) [2.52 (2.28; 2.74)] | 2.59 (0.38) | 0.5014 |
| During exercise | |||
| ΔFO2 max., % | 2.88 (0.57) [2.78 (2.47; 3.11)] | 2.72 (0.41) | 0.2062 |
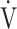 E- E-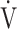 CO2 slope CO2 slope |
39.1 (8.9) | 40.3 (10.9) [39.2 (34.2; 43.2)] | 0.8073 |
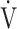 E/ E/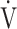 CO2 nadir CO2 nadir |
43.1 (7.9) | 46.8 (7.6) [46.0 (41.0; 50.0)] | 0.0294 |
| Number of patients reaching AT, n (%) | 49 (96) | 51 (72) | 0.0006 |
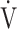 O2 at AT, mL ⋅ min−1 O2 at AT, mL ⋅ min−1
|
601 (178) [575 (490; 670)] | 481(104) | 0.0001 |
| Number of patients reaching RCP, n (%) | 19 (37) | 7 (10) | 0.0003 |
Data are presented as means (standard deviation) or [medians (interquartile range: 25th percentile to 75th percentile)], unless otherwise stated. AT: anaerobic threshold; ΔFO2: difference between inspired mean oxygen concentration and expired mean oxygen concentration; ΔFO2 max.: the highest value during exercise; fR: breathing frequency; HR: heart rate; O2 pulse: 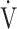 O2/HR; predicted maximum HR: 220−age (y); OUES: oxygen uptake efficiency slope (see the Methods for details); R: gas exchange ratio; RCP: respiratory compensation point; TI/Ttot: inspiratory duty cycle;
O2/HR; predicted maximum HR: 220−age (y); OUES: oxygen uptake efficiency slope (see the Methods for details); R: gas exchange ratio; RCP: respiratory compensation point; TI/Ttot: inspiratory duty cycle; 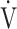 CO2: carbon dioxide output;
CO2: carbon dioxide output; 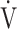 E: minute ventilation; and
E: minute ventilation; and 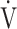 E/
E/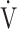 CO2-slope: the slope was determined by linear regression analysis of
CO2-slope: the slope was determined by linear regression analysis of 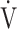 E to
E to 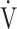 CO2 obtained during exercise (see the Methods for details);
CO2 obtained during exercise (see the Methods for details); 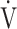 E/
E/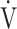 CO2-nadir: the lowest value during exercise (see the Methods for details);
CO2-nadir: the lowest value during exercise (see the Methods for details); 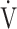 O2: oxygen uptake; VT: tidal volume. Estimated maximal voluntary ventilation (MVV) (L·min− 1) was equal to forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)×35
O2: oxygen uptake; VT: tidal volume. Estimated maximal voluntary ventilation (MVV) (L·min− 1) was equal to forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)×35
