Table 4.
Incremental exercise variables in GOLD III-IV COPD patients divided into two groups by the desaturation level at peak exercise
| Non-desaturation group: 3% or less (n = 23) | Desaturation group: greater than 3% (n = 48) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At peak exercise | |||
| Dyspnea, Borg scale | 5.7 (1.7) | 6.2 (1.9) [6.5 (5.0; 8.0)] | 0.2520 |
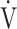 O2, mL⋅min−1 ⋅ kg−1 O2, mL⋅min−1 ⋅ kg−1
|
11.0 (3.0) | 10.5 (1.9) | 0.4505 |
| R | 1.02 (0.10) [1.02 (0.95; 1.07)] | 1.00 (0.07) | 0.7119 |
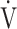 E, L ⋅ min−1 E, L ⋅ min−1
|
30.7 (7.2) | 26.6 (5.9) | 0.0124 |
| VT, mL | 1029 (240) | 967 (238) [917 (794; 1082)] | 0.2796 |
| fR, breaths ⋅ min− 1 | 30.3 (5.2) | 28.2 (5.2) | 0.1058 |
| TI/Ttot | 0.35 (0.06) | 0.34 (0.04) | 0.2806 |
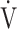 E/ E/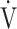 O2 O2
|
49.5 (8.1) | 47.3 (7.0) | 0.2310 |
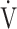 E/ E/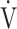 CO2 CO2
|
48.9 (9.8) [48.0 (43.0; 52.0)] | 47.3 (7.6) [46.0 (41.4; 51.0)] | 0.6055 |
1−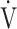 E/MVV, % E/MVV, % |
2.2 (15.9) [10.2 (−8.1; 17.8)] | 11.3 (13.9) [12.7 (3.3; 20.3)] | 0.2169 |
| HR, beats ⋅ min− 1 | 111 (17) | 113 (17) | 0.5799 |
| HR/predicted maximum HR, % | 78.8 (10.4) | 80.6 (11.0) | 0.5280 |
| SpO2, % | 95 (2) | 88 (5) | ND |
| O2 pulse, mL ⋅ beats− 1 | 6.0 (2.1) | 5.1 (1.3) | 0.0818 |
| OUES | 1086 (437) | 1158 (444) [1129 (880; 1345)] | 0.4317 |
| ΔFO2, % | 2.52 (0.39) | 2.63 (0.37) | 0.2839 |
| During exercise | |||
| ΔFO2 max., % | 2.68 (0.43) | 2.73 (0.41) | 0.6083 |
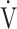 E- E-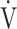 CO2 slope CO2 slope |
41.7 (11.4) [39.1 (34.6; 44.8)] | 39.6 (10.7) [39.3 (34.1; 42.8)] | 0.5972 |
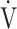 E/ E/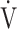 CO2 nadir CO2 nadir |
47.4 (8.1) | 46.5 (7.3) [45.5 (41.0; 49.0)] | 0.6387 |
| Number of patients reaching AT, n (%) | 16 (70) | 35 (73) | 0.7689 |
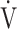 O2 at AT, mL ⋅ min−1 O2 at AT, mL ⋅ min−1
|
515 (144) | 464(78) | 0.1109 |
Data are presented as means (standard deviation) or [medians (interquartile range: 25th percentile to 75th percentile)], unless otherwise stated. AT: anaerobic threshold; ΔFO2: difference between inspired mean oxygen concentration and expired mean oxygen concentration; ΔFO2 max.: the highest value during exercise; fR: breathing frequency; HR: heart rate; O2 pulse: 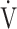 O2/HR; predicted maximum HR: 220−age (y); ND: not done; OUES: oxygen uptake efficiency slope (see the Methods for details); R: gas exchange ratio; RCP: respiratory compensation point; TI/Ttot: inspiratory duty cycle;
O2/HR; predicted maximum HR: 220−age (y); ND: not done; OUES: oxygen uptake efficiency slope (see the Methods for details); R: gas exchange ratio; RCP: respiratory compensation point; TI/Ttot: inspiratory duty cycle; 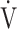 CO2: carbon dioxide output;
CO2: carbon dioxide output; 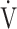 E: minute ventilation; and
E: minute ventilation; and 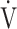 E/
E/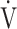 CO2-slope: the slope was determined by linear regression analysis of
CO2-slope: the slope was determined by linear regression analysis of 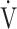 E to
E to 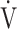 O2 obtained during exercise (see the Methods for details);
O2 obtained during exercise (see the Methods for details); 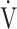 E/
E/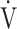 CO2-nadir: the lowest value during exercise (see the Methods for details);
CO2-nadir: the lowest value during exercise (see the Methods for details); 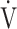 O2: oxygen uptake; VT: tidal volume. Estimated maximal voluntary ventilation (MVV) (L·min− 1) was equal to forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)×35
O2: oxygen uptake; VT: tidal volume. Estimated maximal voluntary ventilation (MVV) (L·min− 1) was equal to forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1)×35
