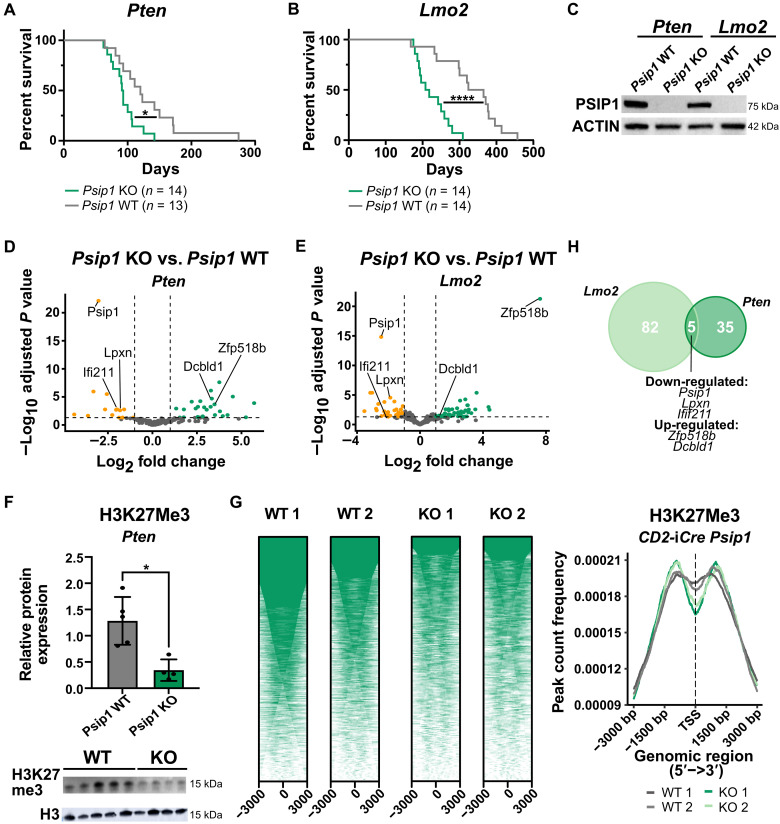
Fig. 2. A tumor-suppressive role for Psip1 in T-ALL tumor initiation.
(A and B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for mice with conditional loss of Psip1 that were crossed with either the Lck-Cre Pten floxed (Pten) model (A) or CD2-Lmo2tg (Lmo2) model (B). The resulting Psip1 KO mice (Psip1fl/flLck-Cretg/+Ptenfl/fl or Psip1fl/flCD2-iCretg/+CD2-Lmo2tg/+) significantly accelerates T-ALL development compared to Psip1 WT (Psip1+/+Lck-Cretg/+Ptenfl/fl or Psip1fl/flCD2-iCre+/+CD2-Lmo2tg/+) (Mantel-Cox test). (C) Western blot validating the complete loss of Psip1 expression in tumor samples derived from the thymus of Psip1 KO and WT mice from both spontaneous T-ALL mouse models (Pten or Lmo2). (D and E) Differential gene expression was performed on thymic lymphoma samples of mice with and without Psip1 expression for both the Pten model (D) (KO: n = 9; WT: n = 6) and the Lmo2 model (E) (n = 6 in each group) (log fold change> 1; Padj < 0.05). (F) Western blot (bottom) and quantification (top) of H3K27me3 protein levels in preleukemic thymus samples of 6-week-old Pten mice, which are Psip1 KO or Psip1 WT, respectively (Mann-Whitney test). Samples were diluted 10 times for H3 Western blot to avoid overexposure. (G) CUT&RUN analysis for H3K27me3 binding in preleukemic thymus samples of 6-week-old Psip1fl/fl/CD2-iCretg/+ (KO) or Cre-negative Psip1fl/fl/CD2-iCre+/+ littermate control (WT) mice (n = 2 for each group). Individual heatmaps (left) and metanalysis (right) of H3K27me3-binding profiles −3 and +3 kb around the transcription start site. TSS, transcription start site. (H) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes upon Psip1 KO in the PtenLck or Lmo2CD2 T-ALL model. Five common differentially expressed genes were identified: Psip1, Zfp518b, Dcbld1, Lpxn, and Ifi211. *P < 0.05 and ****P < 0.0001.