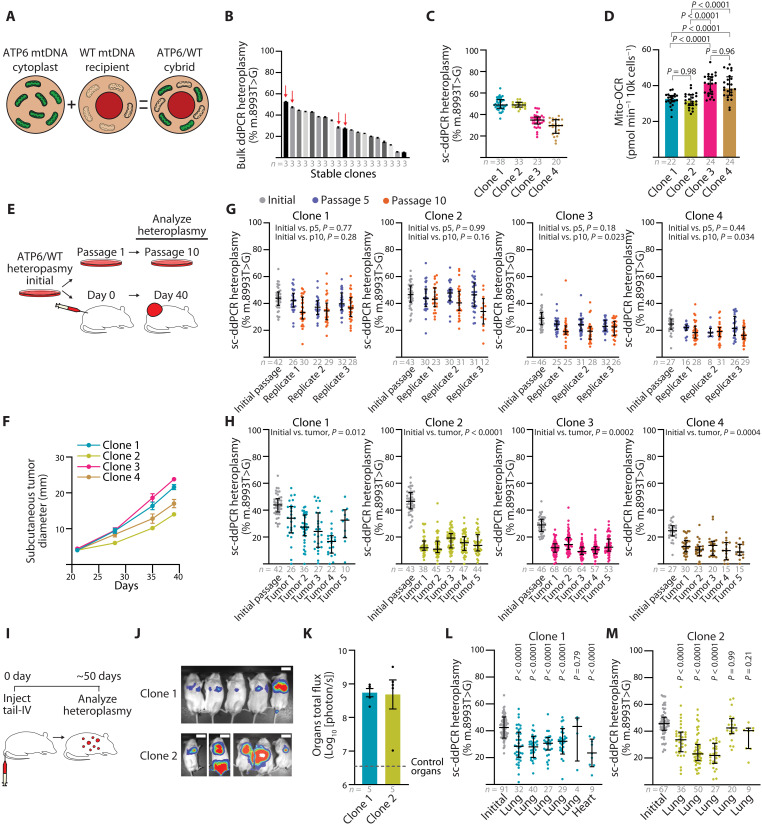
Fig. 7. Purifying mtDNA selection is a feature of melanoma growth.
(A) Overview of the ATP6/WT heteroplasmic cybrid generation. (B) Bulk ddPCR analysis of m.8993 T>G heteroplasmic frequency for ATP6/WT cybrids after clonal line establishment. Data from technical replicates are provided. Clones 1 to 4 selected for experiments are indicated with red arrows. (C) Single-cell ddPCR (sc-ddPCR) analysis of m.8993 T>G heteroplasmy for selected ATP6/WT cybrid clones. (D) Mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate of ATP6/WT heteroplasmic clones. (E) Illustration of heteroplasmic selection experiment. Initial cells were passaged for extended in vitro culture or xenografted for subcutaneous tumors in NSG mice. (F) Subcutaneous tumor diameter over time after xenograft of 100 cells from heteroplasmic ATP6/WT clones. (G) Single-cell ddPCR analysis of m.8993 T>G heteroplasmy for ATP6/WT heteroplasmic clones at passage 5 (p5) and passage 10 (p10) of in vitro culture. Three replicates were independently passaged and analyzed for each clone. (H) Single-cell ddPCR analysis of m.8993 T>G heteroplasmy for ATP6/WT heteroplasmic clones of subcutaneous xenograft of 100 cells following tumor growth. (I) Illustration of heteroplasmic selection assay following tail vein intravenous injection of ATP6/WT heteroplasmic clones. (J) Bioluminescence imaging of live mice following intravenous injection of 1000 cybrid cells. Scale bars, 50 mm. (K) Quantification of organ bioluminescence total flux following intravenous injections. (L and M) Single-cell ddPCR analysis of m.8993 T>G heteroplasmy for ATP6/WT heteroplasmic clones’ tumor nodules following intravenous injection. P values reflect comparisons with the initial passage. The number of samples (biological replicates, unless otherwise indicated) analyzed per group is indicated. Data are mean ± SEM [(B) and (F)] and median ± interquartile range [(C), (D), (G), (H), (K), and (L)]. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison adjustment (D). Nested one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparison adjustment [(G) and (H)], one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparison adjustment (L), and nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison adjustment (M).