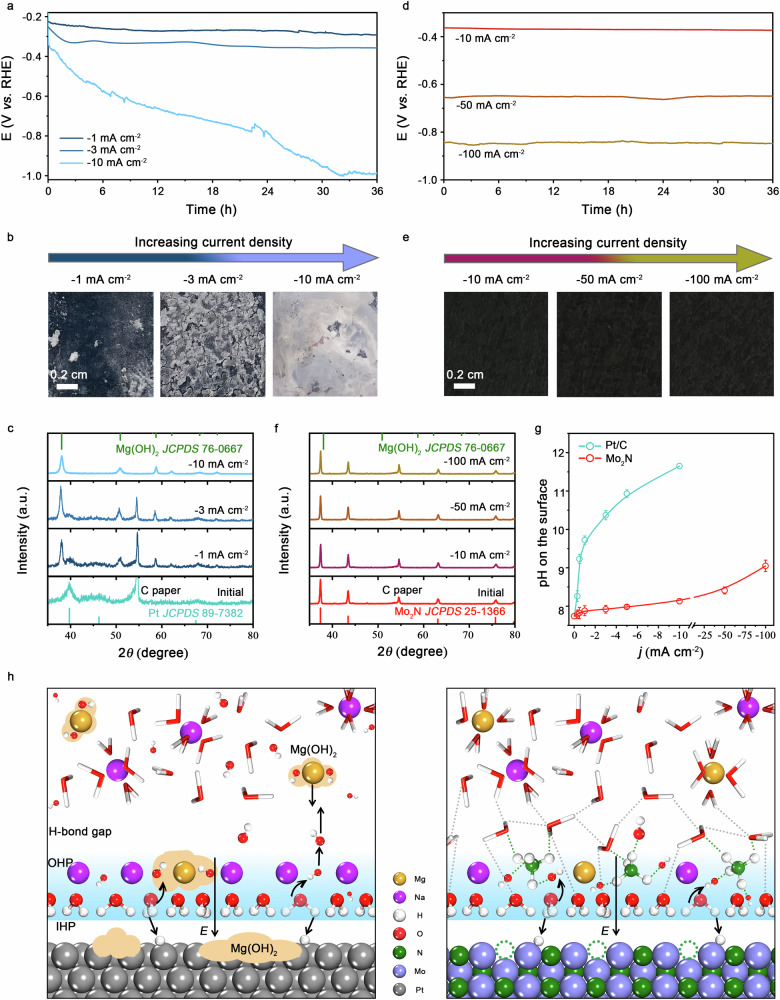
Fig. 3. Anti-precipitation capability of Mo2N catalyst.
a, d Chronopotentiometry curves of commercial Pt/C (a) and Mo2N (d) catalysts operated at different current density in natural seawater. b, e Photographs of Pt/C (b) and Mo2N (e) catalysts on the carbon paper after electrolysis at different current densities for 36 hours in natural seawater. c, f XRD patterns of Pt/C (c) and Mo2N (f) catalysts on the carbon paper after electrolysis at different current densities for 36 hours in natural seawater. g Local pH on the surface of Pt/C and Mo2N catalysts as a function of current density in natural seawater. Error bars are based on the standard deviation of three independent measurements. h Schematic of the NH4+ formation on the Mo2N surface that prevents precipitate formation, whereas Mg(OH)2 precipitate formed on the surface of Pt/C catalyst.